If a mole is often injured, causes aesthetic problems, or has a tendency to malignant degeneration, removal is recommended. Thanks to the use of modern technologies, nevi are excised painlessly, the operation is quick, does not require hospitalization and rarely causes complications.
When a large growth is removed, an inflammatory process occurs and keloid scars may remain on the skin. The scar after mole removal may have a large diameter, dense structure, cause discomfort and create a cosmetic defect.
Mechanism of scar formation
After the wound heals, the epithelium is replaced by connective tissue, which is characterized by increased density and reduced functional properties. There are no hair follicles or sweat glands, and the cells are more susceptible to ultraviolet radiation.
Scars after removal of large moles can be hypertrophic or atrophic. The first type is characterized by excessive growth of collagen fibers; a convex scar occupies a larger area than the size of the former nevus, rises above the surface of the surrounding skin, and looks like a rounded nodule. Atrophic scars, on the contrary, cause tightening of the dermis, and less connective tissue is formed than was previously healthy.
The process of keloid formation begins 2 weeks after epithelization of the wound and continues for several years. During this time, it enlarges, becomes coarser, and changes color from bluish, red to light pink. After 2–3 weeks, the new tissue swells, becomes convex, causes itching, and painful sensations appear on palpation.
After a month, the severe discomfort goes away, the skin around the scar turns red. The scar becomes dense to the touch and acquires an uneven, bumpy surface. After a long period of time, the keloid may become soft or remain hard forever.
Causes of scar formation
Most often, scars form after removal of moles using classical surgery, cryo or chemical destruction. During the treatment, the skin becomes frostbitten or burns; further healing is accompanied by the appearance of scars.
Complications during the rehabilitation period can develop due to poor hygiene, non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations, the addition of a bacterial infection, inflammation, and suppuration. After regeneration of necrotic ulcers, the scars remain deeper and have jagged edges.
There is a genetic predisposition to the formation of a keloid; in such people, the prolongation of any injury is accompanied by a pathological proliferation of connective tissue.
The tendency to form scars is observed with increased production of collagen fibers in the skin.
After laser removal of a mole, scars remain in isolated cases. When exposed to a carbon dioxide ray, the liquid evaporates from the nevus and it is destroyed. There is no bleeding because the blood vessels are cauterized. During treatment, there is no direct skin contact with instruments or the doctor’s hands, this reduces the risk of postoperative infection.
Causes
Doctors have not yet developed a consensus on the reasons for the formation of keloids.
One of the reasons for the formation of keloid tumors is a violation of the integrity of the skin during surgery.
Epithelial tissue grows rapidly due to the excess collagen content in the body. Excess collagen leads to the appearance of a red keloid scar at the site of nevus removal.
On this topic
All about how to care for a removed mole
- Irina Nasredinovna Nachoeva
- August 19, 2021
Experts consider the following factors to be important in the formation of keloids:
- Heredity is one of the main ways of development of many pathological changes in the body. The presence of keloid scars in parents increases the likelihood of the patient developing them after mole removal.
- Hormonal imbalances. The development of connective tissue under the influence of hormonal imbalance can lead to the formation of keloids.
- Careless and improper handling of the wound after mole removal. Under no circumstances can the protective crust be removed or picked out. Such actions are fraught with infection, pathological changes in epithelial tissues, and delayed healing of the wound.
- Damage fresh , healed wound, skin overstrain. This is facilitated by uncomfortable clothes (small, tight, rubbing, etc.), and excessive tanning.
- of collagen in the body leads to the growth of epidermal tissue in excessive volumes.
- Pregnancy period .
- Endocrine system , which works with disturbances.
Treatment options
How to remove a scar at the site of a removed nevus? Cosmetic procedures, the use of special creams, or surgical excision of pathological tissue can help get rid of scars on the face and body.
Laser treatment techniques are widely used. When exposed to the skin, dense fibers are destroyed, the production of fibroblasts is stimulated, connective cells, in turn, contribute to the formation of new collagen, elastin, and smoothing of the dermis. After resurfacing, slight redness of the skin may appear, which goes away on its own after 3 days. The course of treatment consists of 4–5 sessions.
For greater effectiveness after laser therapy, it is useful to do dermabrasion, mesotherapy, facial peels, take physiotherapeutic procedures, and use EPI-DERM silicone film.
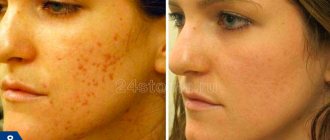
Are red moles dangerous?
In most cases, red moles are not dangerous.
Transformation into malignant formations also occurs due to external factors such as:
- Damage;
- Ultraviolet radiation;
- Internal oncological diseases.
Damage usually occurs in areas in contact with clothing, on the face and head. Trauma to a mole causes bleeding and can be susceptible to infection and may grow and become cancerous.
Also, a red mole can be a sign of cancer, especially if it is cavernous; if it itches, itches and flakes, this means a possible transition to malignancy. In this case, you should contact a specialist - oncologist, dermatologist.
During pregnancy in women, this is a common occurrence, but scratching is still prohibited; doctors recommend making circular movements with your finger with slight pressure.
Danger occurs when angiomas begin to grow on internal organs, thereby disrupting their functioning. In this case, there is a risk of other internal diseases and inflammations.
The spontaneous disappearance of a red mole indicates that the disease process has been eliminated; if, on the contrary, the mole progresses, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Signs of degeneration of a red mole
Scar creams
You can improve the condition of the skin after removing moles with a laser or cauterization using medicinal ointments. Pharmacy products are used at home in the initial stages of scar formation. Absorbable and softening gels are most effective for shallow defects and are prescribed for complex treatment after laser resurfacing.
Creams for scars on the face and body:
- Contractubex has a softening, anti-inflammatory and smoothing effect on scar tissue, inhibits the growth of keloid feroblasts, relieves itching and irritation. The ointment helps remove atrophic and hypertrophic scars after mole removal. The gel is applied 2-3 times a day; for old scars, bandages are applied at night. Treatment is long-term and can take several months.
- Scarguard is a liquid cream made from hydrocortisone, silicone and vitamin E. The drug reduces inflammation, itching and swelling of tissues, and deeply moisturizes the skin. Tocopherol acts as an antioxidant, increases the elasticity of the epidermis, and stimulates cellular metabolic processes. The course of treatment is 1–6 months, the duration of therapy depends on how long ago the excision was performed.
- Kelo-coat is made from silicone. The drug prevents the formation and reduces the severity of scars, improves the aesthetic appearance of the dermis. After applying the gel, a protective film is formed that protects against the negative effects of external factors and liquid evaporation. The scars soften and gradually smooth out.
Healing
A wound is formed at the site where the mole was removed immediately after the operation. Depending on the method of eliminating the defect, either a clear narrow scar or a spot appears on the skin. In most cases, a crust forms in the area where the skin was cut with a scalpel, damaged by laser, liquid nitrogen or electrical exposure. This is a protective reaction of the body aimed at closing an area vulnerable to infection. In the first week - ten days, it is not recommended to carry out any physical impact on the area of the operation. Maintaining the integrity and tight fit of the crust to intact skin protects against infectious complications. Therefore, you should refrain from rubbing, applying bandages and plaster, or rubbing creams. Especially towards the end of the first week, patients are bothered by itching, which causes involuntary peeling off of the crust.
Important! Premature removal of the crust from the wound is fraught not only with infection and an increase in the recovery period, but also with the formation of a more noticeable scar at the site of the operation.
Scar Formation
After removal of a mole, a scar begins to form under the crust. After falling off, young pink skin is found in its place. At first, the scar is painful upon contact, then increased sensitivity, and over time, unusual sensations when touched disappear, and the elasticity of the tissue is restored.
The appearance of an uncomplicated scar also does not cause concern: the pink surface fades over time, the level of the scar is leveled with the general level of epithelial tissue, the skin looks healthy, and the site of damage is not noticeable. Complete healing of the wound surface occurs after removal of the mole in about a year. The scar at the site of surgical treatment or the area of non-invasive treatment is hardly noticeable by this time and practically does not stand out.
What determines the risk of scarring?
The appearance of a scar and its nature depends on a number of factors:
- Depth and area of damage: if they are small, a scar may not appear at all.
- Tissue healing abilities.
- The presence of chronic diseases (for example, diabetes).
- Time for complete healing of the wound (it may increase if the wound has become infected).
The process of complete wound healing, which lasts for 21 days, ends with pathological scarring in only 33% of cases. If the process lasts more than 21 days, the probability increases to 78%.
Complications
In rare cases, the restoration of the integumentary tissue does not go so smoothly.
Cosmetic defect
If for some reason the wound does not heal by primary intention (multiple removal of the crust, repeated trauma to the surgical site), then the scar is not so flawless. The connective tissue spreads over a larger area, and there is a strong decrease in elasticity, which means limited mobility. But, sooner or later, in this case too, the functions will be restored, and healing will occur fully.
Keloid scar
An even rarer complication after mole removal is a keloid scar. This is a very unpleasant consequence that occurs for unknown reasons. It is believed that the following factors can provoke the appearance of excessive skin growths instead of the formation of a neat scar:
- deep damage to the epithelium;
- decrease in the body's immune forces;
- tendency to allergies;
- special conditions, for example, pregnancy, puberty.
But the most significant reason for the occurrence of a keloid scar is considered to be a genetic predisposition. In this case, a hypertrophied growth can occur even without visible tissue damage (in this case we are talking about a tumor of keloid origin) or at the site of the smallest scratch.
Stages of keloid development
A keloid scar does not form immediately after removal of a mole. Against the background of textbook healing, after a year, and sometimes more, the tissue on the scar begins to grow. The connective tissue appears inflamed (red or pink), and the volume quickly increases. The surface of the scar is smooth, but uneven, protruding above the skin by 8 - 10 mm.
The formation of a scar and its growth last on average 2 – 3 years, but can last up to 5. During this time, the fibers of the growth become coarser, and in case of accidental injury, screeds and excessive skin tension are formed. Then the scar stabilizes and remains unchanged for many years. Its increase in a stable period is provoked by accidental repeated damage, constant physical or thermal exposure.
Definition of the term “keloid scar”
The elimination of nevi and other formations on the skin with the modern level of development of medical technologies makes this procedure almost painless and quick. In most cases, the patient does not even have scars on the skin.
In cases where there is a deviation in the healing process of wounds after removal of moles, complications appear in the form of a scar (keloid scar).
The skin in this area acquires a compacted structure in the form of convex tubercles and differs in color from normal (bluish or dark pink).
Laser mole removal
In most cases, moles do not cause inconvenience, and therefore do not need to be removed.
The process of hypertrophic formation is long-term, so the skin heals up to one year, and the scar appears as a compaction within six months. The time it takes for a raised scar to appear is influenced by the size of the sanitized skin area.
After removal of tumors during the first weeks, the skin protects itself by forming a thin layer of epithelial tissue. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, disturbances in the growth of this layer occur.
As a result, epithelial tissue grows and thickens with a color change to a pale shade. Then the tissue swells, and the resulting colloidal tissue grows. The wound hurts and itches, gradually these symptoms go away, and the neoplasm takes on convex, hard shapes.
Treatment of postoperative scars
Uncomplicated healing processes after mole removal do not require special therapy. In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend emollient ointments and creams; in case of a large healing area, a course of physiotherapy is prescribed.
Keloid scar is a complex case. On the one hand, any physical impact can provoke rapid growth of connective tissue. On the other hand, in the absence of treatment, a significant cosmetic, physical and functional skin defect develops. Therefore, in each specific case, dermatologists resort to individual schemes for restoring skin smoothness. Doctors have the following tools in their arsenal:
- absorbable ointments (“Karipain”, “Kotnraktubex”, etc.) - daily rubbing, applying bandages;
- corticosteroids (“Triamcinolone acetonide”, etc.) – injection of a suspension of the drug into the growth approximately once a month;
- physiotherapy (electrical and phonophoresis with the flow of ions of absorbable agents into the tumor area);
- constant grinding of the skin surface - effective at the first signs of a keloid or after its surgical removal;
- excision of scar tissue with subsequent prevention of an increase in the amount of scar connective tissue;
- tight bandaging (bandage) with absorbable agents at the first signs of overgrowth.
Important! Keloid scar is a chronic phenomenon that requires periodic courses of treatment. But with age, aggressive tissue proliferation gradually decreases, and after 40 years it is much less common than in childhood and youth.
The positive point in this situation is that keloids are not prone to degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Thus, the scar after mole removal in the vast majority of cases is neat and does not cause trouble to the person who underwent the operation. In rare cases of excessive scar growth, the dermatologist will select a treatment that is recommended to be strictly followed.
How to remove keloid and hypertrophic scars after surgery. Laser removal. Reviews
The following methods are used to treat keloid scars:
- Injections. Exposure to hormonal drugs limits cell activity and inhibits the growth of connective tissue. The injection is given directly into the scar. After administration of the drug, the keloid loses color. To achieve a positive result, a course of injections is required, which includes 5-6 injections. The likelihood of a positive outcome of therapy increases when injections are used with other treatment methods;
A few days after the procedure, the scar area will become covered with a crust that cannot be removed. Experts disagree about this method of treatment, since the laser can provoke a relapse.
Video: Laser removal of scars and scars
A scar after removal of a mole is a mark on the skin, which consists of connective tissue and is formed when the wound that arose as a result of excision of the nevus has healed. The scar contains a large amount of collagen; the tissues have low functional capacity. The scar is not elastic and has no hair follicles or sweat glands. The stain removal mark is highly sensitive to ultraviolet radiation.
In what cases does a scar remain?
Considering the painless factor of mole excision, removal methods should be used for the following reasons:
- the nevus is subject to constant mechanical damage;
- the location of the growth in a place where friction is increased (the area of the body where hair removal occurs, the bridge of the nose, shoulders, abdomen);
- nevus has a malignant form;
- the presence of aesthetic discomfort from a convex, hanging or large mole.
Scars can form in various parts of the body. There are several types:
- A hypertrophic scar after removal of a mole is distinguished by its elevation above the skin and does not have the ability to spread beyond the area where the nevus was located. After two to three years, the mark from the operation will level out and reach the skin level.
- An atrophic scar is presented in the form of a hole at the site where the mole was removed. The area of the body has a flabby surface.
- After removal of a mole, a keloid scar can rise above the skin level and extend beyond the area where the nevus was removed. Scars of this type are visible to the naked eye, they hurt and begin to itch.
- Normotrophic. The formation of a scar of this type is invisible to other people. It is flat and flesh-colored.
A scar occurs in 80 percent of cases. If the scar darkens, turns red or itches after mole removal, the following factors may be the cause:
- Injury to the place where the mole was removed or the skin around it was stretched. Mechanical impact will provoke the process of tissue proliferation. This may include uncomfortable and tight clothing or prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Trying to get rid of the scar on your own.
- Increased levels of collagen production will lead to the development of excessive epidermal tissue.
- Changes in hormonal levels. A hormonal surge affects the metabolic process in the body, as a result of which connective tissue is formed incorrectly.
- The hereditary factor serves as the root cause if pathology occurs. If a man or woman has a colloidal scar, there is a high chance that their child will experience a similar phenomenon.
- Improper care of the wound surface. After removing the nevus, a protective crust forms. It may itch. It is forbidden to rip it off or comb it, as this increases the risk of infection entering the wound. The excision site will take longer to heal, and pathology will occur in the epithelial tissues.
Serious symptoms
In some cases, it is better not to think about whether it is possible to remove moles on the face, but to rush to the doctor and have them removed as quickly as possible. We are talking about the degeneration of a nevus.
Symptoms that characterize danger are:
- different color;
- increase in size of the mole;
- redness;
- falling hair growing from the roots of the mole;
- cracks are observed;
- the nevus itches or feels burning;
- fluid or blood is released from the mole.
If such manifestations occur, you should immediately seek help from a dermatologist-oncologist. If you feel discomfort in the area of the mole, and the doctor’s advice is removal, do not hesitate. Untimely removal of the nevus can lead to the development of melanoma.
It is very dangerous to self-medicate, use various ointments and folk remedies. This can lead to the development of a pathological process in tissues. It is also strictly forbidden to get rid of moles yourself. The consequence of such an act may be blood poisoning.
Effective ways to get rid of a scar
Surgery during which a birthmark is removed is a serious procedure, so it is recommended to remove the formation not in a beauty salon, but in a specialized clinic. The doctor selects the method of excision individually, based on the characteristics of the nevus. The beauty salon provides laser nevus removal. In rare cases, a scar remains after removal of a mole with a laser, but nevi that are oncological in nature cannot be removed with a laser. It is recommended to entrust the excision of the spot to a surgeon, since improper surgical intervention results in a compaction that rises above the level of the skin.
If you have a question about how to remove a scar after removing a mole, avoid self-medication. It is advisable to visit a doctor who will prescribe medications that can get rid of the scar. This is required for those nevi that are located on the face, as the person’s appearance changes. Medical removal of scars is based on the use of cream, ointment, gel, which are applied to the place where the formation was located.
A popular medication is Contractubex. The gel has an anti-inflammatory and relaxing effect, restores the epidermis. Duration of use is at least three months. During this time, it is necessary to apply the gel to the area of skin where the stain was removed. Continue application until the scar completely disappears. Application time depends on skin and health.
An effective way to get rid of scars is dermabrasion. Mechanical peeling is based on grinding the area of skin where the growth was located. Sanding is done using a rotating brush. Dermabrasion eliminates scars in the upper layer of the skin, reducing the risk of deep scarring.
To eliminate the mark after excision of a nevus, injection of collagen or fat mass is necessary. The method is effective for small scars. The process is based on filling the area of skin with a scar with a special substance. After the procedure, the scar becomes almost invisible. In addition to eliminating scars, injection treatment involves rejuvenating the dermis and accelerating the recovery process. As a result of mesotherapy, the skin acquires an elastic, firm, toned appearance. The disadvantage of mesotherapy is the short duration of the effect. A month later, the injection must be repeated. This method is used less frequently than others due to its high price.
Laser removal stimulates the growth of a new layer of skin. To achieve the result, it is necessary to carry out three to four procedures, after which the scar will become less noticeable. Laser therapy is carried out using two methods:
- The impact of laser beams on blood vessels, the flat scar disappears.
- The laser beam heats the surface of the skin to remove the epidermis. The advantage of the method is that there is no risk of infection, and the time during which the skin recovers after therapy.
The surgical method of removing a scar after excision of a nevus is one of the most difficult. The surgical procedure using a scalpel involves sewing new skin onto the area where the growth was located. The method is time-consuming and expensive. Surgical removal is recommended if twelve months have passed since the birthmark was removed.
Types of moles
As any medical reference book says, a nevus is a skin formation that appears at birth. In special cases, it is acquired during life. These formations are benign. They do not require removal or treatment. But over the course of a person’s life, they can become malignant tumors. This may be accompanied by influences both externally and internally.
All nevi are divided into several varieties:
- Flat. These moles are pigment spots that every person has. Visually they look like dots. Their color can vary from bright brown to dark shades. Such nevi do not grow and do not threaten human life. Is it possible to remove flat moles on the face? Doctors say that it is almost always possible to get rid of such nevi.
- Convex. These are protruding skin formations. They differ from ordinary moles by their bumpiness. This species is unsafe for human life. Therefore, people with such moles need to see a doctor. And only a doctor can say whether it is worth getting rid of such nevi.
- Blue. These moles are a special type. They are considered safe. Consultation with a doctor is necessary only if the nevus increases. Blue moles can come in different shapes, sizes, and consistencies.
- Vascular. This type occurs on the human body from the upper layer of skin. Vascular moles are warts. They pose a danger only if they grow very quickly or are at the epicenter of inflammation.
What method of mole excision does not leave scars?
Regardless of which method was used to remove the growth, there should be no trace left. There are cases where a colloidal scar occurs due to the excessive appearance of new skin cells in the wound. The reason for this is a violation of excision technology or epidermal pathology. Electrocoagulation, which affects the formation of high-frequency current, leaves a small scar. If the operation is performed correctly, the scar is almost invisible.
Excision of a birthmark using a scalpel is based on the removal of the birthmark and healthy skin. After the procedure, the doctor puts a suture, which leaves a scar. There are no traces left during cryodestruction. The condition is not the facial location of the nevus. This is explained by the fact that liquid nitrogen will damage healthy skin.
Methods for removing a mole without a scar: expert advice
How to remove a mole without scarring? Scalpel, nitrogen, electrocoagulation, laser and even radio wave surgery - according to doctors, none of these methods can guarantee perfect healing.
The cryodestruction method has earned good reviews - it does not leave scars. But moles on the face cannot be removed in this way, since there is a danger of the substance affecting healthy tissue.
Experts advise taking a serious approach to choosing the institution where the removal will be carried out. Two weeks before surgery you need to drink the following complexes:
- multivitamins;
- dietary supplements with silicon, cobalt, iron, copper, selenium, zinc;
- drugs to improve microcirculation - Teonicol, Capilar;
- means for strengthening the walls of blood vessels: Ascorutin, Etamzilat.
During the same period, it is necessary to observe a regime of wakefulness and rest. Moderate physical activity also has a positive effect on microcirculation.
The least invasive methods are laser therapy and electric knife. After removal, you must follow all recommendations given by your doctor.