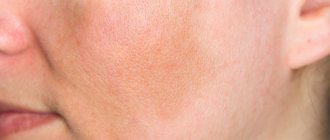
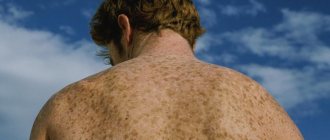
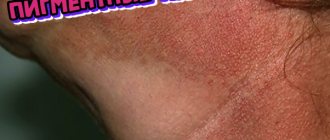
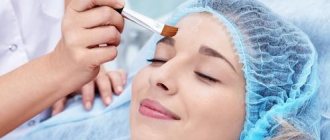
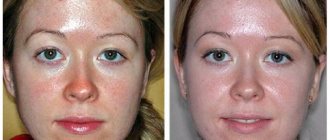
Spots that differ in color from the main skin tone can appear on any part of the body for various reasons. One of the most common is senile lentigo. Such pigmentation disorders are typical for older people. Such spots do not harm a person’s health, but they do spoil the appearance. Modern cosmetology has a sufficient number of tools and methods to successfully eliminate the defect.
General information
Senile (senile) lentigo is the appearance of isolated pigment spots on the skin. The condition is directly related to exposure to UV radiation, and is more common in people with fair skin who live in hot climates.
Age-related lentigo usually appears in patients over 50 years of age. According to medical statistics, 90% of people after 60 years of age develop at least one hyperpigmented area of skin. If there are a lot of spots, the person is diagnosed with lentiginosis.
Dermatologists have not yet come to a definitive conclusion whether lentigo is a precursor to melanoma. It has now been established that malignancy of spots occurs extremely rarely. A possible relationship between skin cancer and senile spots is considered a factor in cancer alertness. The patient is recommended to be monitored by a dermatologist and periodically use self-diagnosis methods.
Signs of degeneration of lentigo maligna into melanoma
Color spectrum of the danger of lentigo maligna in descending order:
- Brown color is characteristic of relatively “quiet” lentigo;
- Black color indicates the beginning of degeneration, the presence of atypical cells;
- Bluish and purple - the formation is transforming into melanoma.
Like all precancerous conditions, Dubreuil's melanosis can grow for years, followed by a rapid onset of melanoma, the so-called. "period of vertical growth."
The process of transformation of Dubreuil's melanosis into melanoma takes from 2 to 30 years on average (most often 10 years). Do not expect that there will be no malignancy
The following symptoms indicate the transformation of lentigo into melanoma:
- The shape and size of the formation begins to change. The edges are no longer clearly defined, wavy and scalloped contours appear;
- The color of the formation changes, new tones appear.
In order to understand the essence of what is happening, it is advisable to visit an oncologist before vertical growth begins. In this case, the doctor will be able to compare what was with what is present. This allows you to significantly speed up diagnosis.
- Scars, dots, and nodules appear on the surface of the spot. Itching and bleeding may occur.
Causes of senile lentigo
Age-related areas of hyperpigmentation appear in older people under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The spots may appear immediately after sunbathing or may result from the accumulation of melanocyte cells. This occurs due to a disruption in the synthesis of melanin, the pigment that determines skin color and is responsible for protecting the skin from sunlight.
Additional factors that provoke lentigo are:
- liver diseases;
- genetic predisposition;
- hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- poor immunity;
- sunburn suffered at a young age;
- excessive sunbathing on the beach or in the solarium;
- human papillomavirus;
- alcoholism;
- diseases of the digestive tract.
In women, lentigo often appears during menopause, against the background of hormonal imbalance in the body.
Diagnosis of the problem
Dermatoscopy is a mandatory procedure if a malignant tumor is suspected
First of all, it must be done by the patient himself. If you have age spots, try to examine them in natural light at least once a week.
If you are unable to assess the condition of the stain yourself, ask family members or friends to do so.
If there are any suspicious changes, contact the oncology clinic.
The doctor, seeing such a formation, tries to immediately conduct a dermatoscopy.
The process involves examining (and photographing) the formation under high magnification. The boundaries of the spot and its surface structure are assessed.
As a rule, a particle of the formation is taken for histological examination. In addition to atypical (malignant) cells, protein tumor markers characteristic of melanomas are determined.
Symptoms of senile lentigo
Age-related lentigo usually does not cause any physical discomfort and is purely an aesthetic problem.
The spots have several distinctive features:
- color from light yellow to dark brown;
- diameter no more than two centimeters;
- round or oblong shape;
- the contours are blurred;
- no signs of peeling, itching, or formation of ulcers;
- the darkenings do not merge with each other, they are located separately.
Senile lentigo in most cases is localized in open areas of the body: face, arms, shoulders, décolleté. Less commonly, marks may form on the back or genitals.
Microscopy of the scraping reveals hyperplasia (increase in size) of melanocytes, especially in the lower (basal) layer of the epidermis.
Despite the fact that this form of hyperpigmentation extremely rarely becomes malignant, the spots should be examined regularly, preferably in natural light. When they are located on easily accessible areas of the skin, you can do this yourself; if not, turn to relatives for help.
You should be wary if you notice such signs as:
- sharp growth of the spot;
- color change;
- the appearance of nodules;
- cracking;
- pain on palpation;
- convexity of the pigmented area.
Attention: when at least one of the listed symptoms is present, you need to urgently visit a dermatologist!
You must make an appointment if you experience any uncharacteristic sensations in the area of darkening. The specialist will conduct an examination and prescribe adequate treatment.
Lentigo melanoma
Ahh, Moscow
334 views
February 18, 2020
A month ago, I removed a mole with an indentation of ~2 mm from the edge, submitted it for histology, and then for a second one, due to mistrust.
1. Unim. Zhuravlev A.S. Maxim Untesco Localization of melanocytes: epidermis (junction), dermis Localization of melanocytes in the epidermis (junction): lentiginous proliferation Localization of melanocytes in the dermis: in the form of nests, scattered cells Cytological characteristics of melanocytes: with signs of cellular atypia Signs of cellular atypia: large nuclei with large nucleoli Phenomenon maturation: present Resection margins: free from nevus cells Distance to the lateral margin of resection: 1.5 mm Conclusion: Dysplastic melanocytic nuvus high-grade D22 / ICD-O C440-C449 / 8727/0 2. Hemotest. Mordovtseva Veronika Vladimirovna In histological preparations under numbers 2551-1-1, 52551-2-2/20 - a skin flap with subcutaneous tissue. The epidermis is flattened, with lentiginous proliferation of atypical melanocytes in the basal layer, with the formation of asymmetrical, rare nest-clefts, with the involvement of the epithelium of hair follicles in the process. Melanocytes with signs of pronounced cytological atypia, stellate shape, with hyperchromatic nuclei. In the dermis there are small accumulations of nevus cells. Mild solar elastosis; focal inflammatory infiltrates. Removed within healthy tissue. Conclusion: D03.6 Lentigo melanoma in the horizontal growth phase. Level of invasion according to Clark I (in situ). Questions: 1. Can the conclusions be erroneous, in the sense that this is melanoma of some third stage or metastasis, and the focus is in a different place? Where can I get a third opinion and who can I look for a hearth in Moscow? Why wasn't melanoma found in unim? Maybe IGH analysis is more accurate? 2. Is it possible to do additional excision 1 cm from the scar or is it too late? A month passed - 2 histologies, 2 weeks each. 3. What examinations are needed? PET CT, MRI, ultrasound of all lymph nodes, biopsy, blood tests (for what?). Could this show anything? Pavlenko did not show metastases throughout the body, only an exploratory operation, maybe I need this too? 4. I have about 10 more seemingly dysplastic moles and about 40 borderline lentiginous moles - should they be removed too? 5. I have had a temperature of 37.5 for six months, and bad tests, lymphocytosis. And also weakness, drowsiness (I sleep 11 hours and don’t go outside, but I’m like a vegetable) and depression. How can you find its cause? I have been taking the immunosuppressant Sandimmun Neoral for a year at a dose of 4 mg/kg (first 9 months) to 2 mg/kg (2-3 months). For the first six months I was constantly sick, until I transferred to home work. I plan to continue drinking Sandimmun. Hemoglobin 146g/l Red blood cells 5×10*12/l Hematocrit 44.8% Mean erythrocyte volume (MCV) 90fl Average Hb content in erythrocytes (MCH) 29.2pg Mean Hb concentration in erythrocytes (MCHC) 326g/l Color index 0.88 Platelets 294×10 *9/l Leukocytes 7.86×10*9/l Immature granulocytes 0.02 10*9/l Immature granulocytes % 0.3% Segmented neutrophils 2.93×10*9/l Segmented neutrophils % 37.3—% Eosinophils 0.25×10*9/l Eosinophils % 3.2% Basophils 0.09++x10*9/l Basophils % 1.1++% Monocytes 0.55×10*9/l Monocytes % 7% Lymphocytes 4.04++x10*9/l Lymphocytes % 51.4++% ESR (Westergren) 2mm /hour 6. Maybe there’s something else I should know that I didn’t ask? Chronic diseases:
atopic dermatitis colloid (?) thyroid nodules / low T4 endometriosis immunodeficiency low-grade fever hair loss (drug remission with immunosuppressants) Epstein-Barr
The question is closed
weakness
low-grade fever
melanoma
lymphocytosis
Prevention of senile lentigo
“Liver” spots on the face of older people are often the result of improper care and lifestyle in youth.
To avoid senile lentigo, you need to follow the following rules from your youth:
- Avoid excess exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Use sunscreen at any time of the year;
- do not get carried away with the solarium;
- in summer, wear light-colored clothes made from natural fabrics and cover your shoulders;
- wear hats with wide brims.
Dermatologists also advise eating right and giving up alcohol and smoking. Bad habits themselves do not lead to lentigo, but they have a detrimental effect on metabolism in general. The result of metabolic disorders can be, among other things, hyperpigmentation.
Senile lentigo is a harmless phenomenon for the body. However, it brings great psychological discomfort, especially to women. You can get rid of the defect if, at its first manifestations, you consult a dermatologist and undergo the prescribed course of treatment.
Causes
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause lentigo. With a high probability, the formation of pigment spots will be noticed in a person who:
- has fair skin;
- was often exposed to direct sunlight or had cases of sunburn;
- sunbathed in the solarium;
- underwent radiation or phototherapy.
In other cases, an inherited syndrome can cause lentigo to develop. The risk group includes representatives of both sexes and all ages. Nuclear or chemical radiation may also be the cause.
Treatment of lentigo
Effective treatment for lentigo comes down to three main components:
1. Daily whitening of the skin defect using special medications;
2. Regular use of special sun protection products;
3. The use of cosmetic procedures to enhance desquamation (exfoliation) of the epidermal layer or the use of photodestruction techniques for cells that contain melanin. The treatment of all types of pigmentation is described in detail here.
To whiten lentigines, it is recommended to use arbutin, azelaic acid or licorice extract. All these substances contain ascorbic and kojic acids, as well as hydroquinone and retinoids. In modern products, hydroquinone is contained in low quantities due to its detrimental effect on melanocytes. The remaining components do not cause side effects and are well tolerated by any organism.
One of the methods of surgical treatment of lentigo is to cut it out from the surface of the skin. This method is indicated if the tumor tends to recur. For this purpose, the surgeon also captures part of the unaffected tissue in order to completely prevent its reappearance. The remaining scar can be removed with plastic surgery.
For those who want to get rid of lentigo without a scar, the laser therapy method is suitable. The laser beam is directed precisely at the tumor, and healthy tissue is not damaged, and therefore there are no postoperative complications. Devices for treating tumors using laser allow you to regulate not only the power of the beam, but also the depth and width of penetration under the skin.
Laser destruction is absolutely painless and does not require the use of local anesthetics. During the procedure, the patient may only feel a slight burning sensation. Immediately after removal of the tumor, slight redness may occur in the surrounding skin. If a person is prone to allergic reactions, then it is possible that slight pigmentation may appear at the site of the intervention.
Before the procedure, the patient must undergo a series of tests to determine any contraindications for the use of laser destruction.
If a specialist has accurately determined that the patient has a benign neoplasm - lentigo, and not melanoma, then you can try to resort to phototherapy. Its essence boils down to exposing the problem area of the skin to a beam of intense light. This should stimulate the tissue to synthesize collagen. In this way, regenerative processes occur that contribute to skin rejuvenation by reducing its compaction.
Medium chemical peels of the epidermal layer are suitable for patients with light-colored tumors, since in addition to removing pigment in the lentigo area, the procedure also lightens healthy tissue.
These include: retinoic peeling, TCA peeling, ABR peeling, pyruvic peeling, azelaine peeling.
Tags: skin diseases
Market Analytics
- 2020 in the beauty industry – innovation without borders
- Black Lives Matter movement: reaction and consequences for the beauty industry
- COVID-19 is changing the rules of the game in the cosmetics market
Convenient search for beauty salons on our website
Beauty salons in Moscow Beauty salons in St. Petersburg Beauty salons in Ekaterinburg Beauty salons in Novosibirsk
Latest blog posts on our website
- Naturecream / Arnica - the magical plant of alchemists
- Naturecream / Tremella Extract - Snow Mushroom Detox for Skin
- Prostye-sovety / How to visually enlarge your lips with makeup
- Naturecream / Apricot kernel oil for face
- Naturecream / MATRIXYL3000 - the best skin elasticity stimulator
- Naturecream / SPF in Natural Oils
- Naturecream / Geranium (Pelargonium) oil for skin health and beauty
- Prostye-sovety / Save on a beauty salon: procedures that can be done at home
- Naturecream / Growth Factor - brings back youth?
- Oksana-Lezina / 3 effective abdominal exercises from a fitness instructor for beginners
Latest forum topics on our website
- Natalya / How to properly make a gelatin mask?
- Mrs._Smith / Badly sunburned! What to do?((
- Ice / Is it necessary to combine fitness classes with a diet?
- Antonova / What can be used for hair loss?
- Radio operatorKat / Who was on a protein diet?
Other articles in this section
| Atopic dermatitis: causes, symptoms and treatment Atopic dermatitis is the most common allergic skin lesion, caused by a combination of a group of hereditary factors. As a rule, the disease develops in early childhood and has a chronic course with periodic exacerbations that occur in response to specific and nonspecific allergens and irritants. |
| Dehydration of the epidermis Dehydration (dehydration) is the cause of many skin diseases, but is not a disease in itself. As a result, diagnosing dehydration is a particular challenge. |
| How to remove swelling from the face: methods and decongestants Edema can occur for various reasons: lack of sleep, increased emotional stress, stress, excess fluid in the body, kidney problems. In any case, this phenomenon is not very pleasant, especially when the symptoms appear on the face. How to get rid of edema using folk methods, cosmetic methods, and medications, we will talk in the article. |
| Photosensitivity of the skin An important role in determining the effectiveness of a particular treatment is played by establishing the cause of skin disease associated with pigmentation - this is the first task that a doctor must solve to draw up an effective treatment plan. If the disease is caused by taking medications for external or internal use, such as corticosteroids or birth control pills, then positive results cannot be guaranteed until the use of the medication is stopped. |
| New trends in the use of botulinum toxin in dermatology In this article we present the results of the work of a group of Italian scientists who studied new protocols for the use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of various types of skin diseases. |
| How to rejuvenate the skin around the eyes? The first signs of aging appear already at the age of 25–30, when wrinkles begin to form around the eyes. This area of the face contains little subcutaneous fat and is highly sensitive. The skin around the eyes is thin and delicate, has few sebaceous and sweat glands, and therefore very often suffers from a lack of moisture. In addition, frequent muscle contraction leads to the formation of facial wrinkles in this area. |
| How to get rid of enlarged pores on your face There are four skin types: dry, combination, normal and oily. Those with oily skin are somewhat lucky - they don't have to worry about extra moisturizing their face. This type is less susceptible to aging, wrinkles appear much later than those with dry or normal skin. In winter, sebum protects the face from the negative effects of low temperatures and cold wind. |
| Nail fungus: causes and how to avoid getting infected? Nail fungus or onychomycosis is a disease that occurs when the nail plate is damaged by a fungal infection. Onychomycosis affects 5 to 15% of people. The risk of its development increases with age, although the fungus is often detected in children. Every 10 years of life, the incidence increases 2.5 times. If in children it is 3%, then in older people it is already 50–60%. |
| Psoriasis: causes, symptoms, classification, stages and severity Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious recurrent disease of autoimmune origin, affecting mostly the skin and its appendages, and to a lesser extent the joints. Both men and women are equally susceptible to the disease. More often the disease manifests itself after 30 years, there have been cases of congenital psoriasis. The disease occurs with remissions of several months or several years, exacerbations often occur in the autumn-winter period. |
| Laser removal of papillomas Laser removal of papillomas is an absolutely safe and effective way to get rid of skin lesions located on any area of the skin, including the face. |
Treatment
Lentigo is usually not removed for medical reasons . But many people want to treat them for aesthetic reasons. Doctors may recommend several techniques to remove stains.
The use of any external agents is permissible only in the case of benign lentigo. For local treatment, creams and ointments are used: Azelik, Tretinoin, Iklen.
- The medicinal method is the use of creams with a whitening effect containing retinoids (Tretinoin, Lokacid, Retinoic ointment).
- Chemical peeling using glycolic, lactic, salicylic acids.
- Laser or intense pulsed light therapy to destroy excess melanocytes.
- Freezing (cryotherapy) to eliminate pigment cells.
When treating solar lentigo, it is necessary to isolate the affected skin from ultraviolet rays.
Technologies of modern medicine allow the removal of unpleasant pigment spots using laser therapy. The laser procedure not only makes the skin more youthful, but also has a number of additional advantages:
- restores the structure of the skin;
- eliminates skin injury;
- there is absolutely no risk of infection;
- Only pigmented areas are directly affected;
- relapses are excluded.
Causes of lentigo
1. The appearance of lentigo is associated with excessive insolation, which can provoke uncontrolled division of melanocytes. These are special skin cells that produce the substance melanin, which causes tanning. They protect the skin from burns and general overheating of the body.
2. Uneven distribution of increased concentration of pigments in the upper layer of the skin, which causes the appearance of a benign neoplasm, can occur for various reasons. Among them are:
• Endocrine disorders, in particular during pregnancy, menopause, disruption of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
• Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
• Metabolic disorders due to lack of beneficial vitamins and minerals;
• Injuries;
• Severe intoxication;
• Inflammatory processes in the skin of various origins.
3. Mutations in genes.
Kinds
There are several types of lentigo, including melanoma, which can also occur on the face. Therapy depends on the type of pathology. For this reason, it is important to determine the type of pigmentation.
Sunny
Solar lentigo occurs under the influence of ultraviolet rays. Most often, pathology is observed in people living in the southern regions, as well as in people with a light-colored epidermis. Typically, formations appear on the face and those areas of the body that are exposed to sunlight.
Typically, pigmentation occurs after a long stay in a solarium or after a sunburn.
This type of lentigo is not considered a pathology of the epidermis. Such spots are considered a cosmetic problem. To prevent pigmentation from occurring under the influence of sunlight, it is not recommended to go outside without applying a protective agent.
Simple or youthful
This type of rash appears immediately after the birth of a child or in early childhood. Spots can appear on any part of the body or mucous membranes, but are most often localized on the lips or head of the genitals in boys. Such lentigines do not pose a threat to the child’s life, since they do not become malignant.
Juvenile rashes appear singly or in groups. The color of the spots ranges from light to dark brown. The reasons for the appearance of formations have not been established. However, it is known for certain that juvenile lentigo does not occur under the influence of sunlight.
Senile
Senile lentigo appears in old age. The spots indicate age-related changes in the epidermis. Formations usually occur in those areas that have been exposed to ultraviolet radiation - the face, hands, décolleté and others. Read more about age-related pigmentation here.
Sometimes this type of rash may indicate the presence of liver pathologies. A doctor can understand the cause of formations after conducting appropriate examinations.
The spots of this type of lentigo do not have clear boundaries. The diameter of the rash reaches up to 1 cm.
This type of rash can become malignant. For this reason, senile lentigo is not recommended to be ignored.
Ink spot lentigo or reticular melanotic lentigo
This is a malignant form of pathology. In this case, the spots are localized on the person’s face or body and have a black or dark brown tint. Education has no clear boundaries.
If left untreated, the spots can lead to death of the patient. Treatment for lentigo is prescribed by a professional. Any independent measures can lead to serious consequences.
Puva lentigo
This pathology occurs due to long-wave ultraviolet radiation. Characterized by the appearance of small spots of uneven shade. Usually the rashes appear in groups on different parts of the body, as well as on the face.
The formations appear in most cases in patients who have undergone PUVA treatment. Such rashes can develop into malignant melanoma, so the spots should not be ignored.
Lentiginosis of the mucous membranes or genital lentiginosis
With this type of lentigo melanoma occurs on the mucous membrane of the mouth or genitals. At the same time, studies show that the number of melanocytes in the skin does not exceed the normal value.
Hereditary or congenital lentigo
This pathology is characterized by the appearance of small, round, brown spots on the epidermis. The formations appear in groups and can occupy a significant area of the epidermis. This type of lentigo usually does not appear on the face.
Treatment with folk remedies
Traditional methods in this case pursue one goal - whitening. It is impossible to influence melanocytes and remove spots in this way.
Pour a tablespoon of low-fat cottage cheese with 3% peroxide and ammonia (2 teaspoons each). After mixing, apply the application to the stains. After 20 minutes, wipe the lentigo with calendula leaves.
Mix a dessert spoon of clay (white) to form a paste with fresh lemon juice, apply to the stains (up to 30 minutes).
Lemon, rowan, grapefruit, and pomegranate juices can have a good effect. You just need to lubricate the stains with them 2-3 times a day. For the same purpose, black currant juice, birch and cucumber juices are used.
What is lentigo?
Lentigo belongs to the category of skin diseases in which on the dermis, regardless of the area of the body, there are lesions in the form of pigment spots of irregular or round shape: yellow, dark yellow and brown.
The development of lentigo at an early stage begins with the appearance of small dots, so the disease has some similarities with freckles. However, as the pathology develops, it increasingly acquires its own features. A feature of the disease is its development and ability to degenerate into individual neoplasms, which in turn is dangerous for the development of oncology.
Development mechanism
The formation of a spot in its mechanism is explained by the beginning of the development of a process in which hyperpigmentation increases sharply, affecting the skin area against the background of a biochemical lesion. Melanin is a substance that is present in the skin, under the pressure of an aggressive environment (resistance to the manifestations of exogenous and endogenous factors), it tries to resist changes in the dermis by activating the protective properties of the body. When it accumulates, it initially forms spots on the surface of the skin, which in their format are easily confused with freckles.
Early pathology in its development mechanism resembles the appearance of freckles, which usually appear against the background of solar activity. Birthmarks and moles differ in the mechanism of development, although these skin formations are often perceived by non-professionals as skin lesions of lentigo or chloasma - a disease in which the skin undergoes hyperpigmentation of a certain area of the skin.
How dangerous is lentiginosis?
Skin diseases are divided into a safe format of manifestations and those whose development cannot be called non-threatening. The pathological effect of lentiginosis on the body is that, under the influence of excess pigments, cell degeneration begins. The development of a spotted neoplasm can be observed by a change in its color and size, at which the transition of the disease to other stages is possible.
The most alarming factor that can be observed during cell reconstruction is the transformation of the spot into a focus of a malignant nature. There are no characteristic factors that indicate this moment; lentiginosis from a state of pigmentation to a malignant neoplasm can pass at any stage of development. Additional dangerous and unpleasant symptoms are:
- The appearance of itching, which can bother you at any time of the day.
- Bleeding.