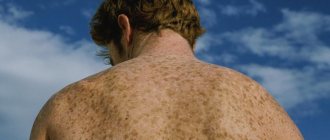
Skin pigments
The color of human skin depends mainly on the quantitative ratio of five important pigments: melanin, melanoid, carotene, reduced and oxidized hemoglobins. Oxygenated hemoglobin in capillaries and arterioles gives the skin a pink or reddish color, and the venous network gives a bluish tint.
Melanin pigment
Despite the fact that skin color is made up of many components, melanin is considered the main pigment of the skin. Melanin in the epidermis and stratum corneum makes the skin light brown, brown or black depending on its quantity and distribution. Although skin pigmentation disorders have a different nature, in cosmetology practice most often there is a need to act specifically on melanin pigmentation.
Why is the sun dangerous?
Melanogenesis is triggered by the synthesis of melanin from amino acids such as L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine with the involvement of many enzymes (the most basic is tyrosinase). The level of pigmentation largely depends on the activity of melanocyte cells and their number (Lerner, Fitzpatrick 1950).
Melanin production has a protective function in the skin and serves as a shield against solar radiation that leads to photodamage. Photodamaged skin responds by thickening the epidermis and increasing melanin production. This is how the body tries to protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation, and it is not surprising that after active recreation, cosmetology clinics are filled with patients with this problem (Gonzaga 2009).
From the point of view of phototoxicity, the most dangerous is the UVA spectrum (320–400 nm), the rays penetrate deep into the layers of the hypodermis and destroy collagen and elastin. The UVB spectrum (280–320 nm) mainly affects the outer layer of the skin - the epidermis. But when combined, both spectrums cause burns and mutagenic effects, including pigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation (also known as hypermelanosis, dyschromia, melasma, melanosis) is a violation of the process of melanogenesis in the direction of increasing skin color. This is how the reference book on skin diseases defines this pathology. However, there is no single classification of hypermelanosis, just as there is no single name for this group of skin pathologies.
In clinical practice, it is convenient to group melanoses according to various criteria:
- By origin - congenital and acquired.
- By prevalence - localized and generalized.
The problems of hyperpigmentation are very complex and controversial. There are many causes of hyperpigmentation, from pregnancy to parasitic diseases and syphilis.
What can modern cosmetology offer?
Photodamage, photoaging, and pigmentation have been shown to be closely related. And this fact should be taken into account when choosing cosmetic procedures - it is necessary not only to remove external manifestations (actually unpleasant areas of darkened skin), but also to act deeper, preventing the initiation of deep destructive aging processes in the dermis.
Treatment algorithm for hyperpigmentation
- After assessing the severity of pigmentation, the cosmetologist can offer several correction options.
- For selected lesions or as protection: combination of topical agents with a high SPF sunscreen.
- For moderate pigmentation: external chemical peeling, non-ablative low-intensity laser.
- For intense pigmentation: fractionated radiofrequency, Q-laser or picosecond laser, non-ablative high-intensity laser, microneedling, IPL system.
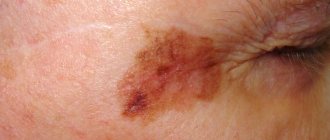
Chloasma
Pigment spots caused by internal causes are called chloasma. They are characterized by an irregular shape and dark color, the intensity of which intensifies before menstruation, as well as a tendency to grow and spread.
Chloasma on the cheeks is often caused by chronic liver diseases. Spots on the side surface of the cheeks are due to hormonal changes, pigmentation around the mouth allows one to suspect a helminthic infestation. If pigment spots are located all over the face, then most likely the problem is related to a malfunction of the adrenal glands.
Pigment spots after sun exposure
Pigment spots appear under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Mineral oils and citrus essential oils (bergamot, orange, lemon) increase skin sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
Post-traumatic pigmentation
Pigment spots can also appear at the site of infiltrates and stagnant spots after acne and injuries. They are called post-traumatic or post-inflammatory.
Some medications can also provoke hyperpigmentation, such as tetracycline antibiotics, salicylates, St. John's wort extract, etc.
The darker the skin, the more carefully it must be handled: any traumatic injury can lead to a worsening of the situation, since the melanocytes of dark skin are very active.
What are pigmented skin diseases?
This category includes skin conditions associated with excess melanin accumulation, such as melasma, solar lentigo, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, chloasma, photoaging (Ogbechie-Godec, Elbuluk 2017).
According to domestic dermatologists, during a month of active practice, at least ten patients with the problem of age spots turn to them for professional help (Kasikhina 2011).
Sun-exposed areas of the skin of the face are usually affected, but there have been cases of involvement of the skin of the hands and other areas of the body.
As the word “hyperpigmentation” implies, this skin condition is characterized by increased production of the melanin pigment, caused by various factors, and primarily by solar radiation.
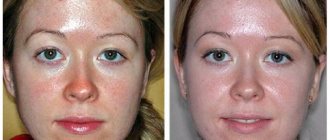
Treatment of hyperpigmentation
There are no special methods for treating this or that melanosis. All cosmetic manipulations are aimed at reducing the color intensity.
Whitening pigment spots
Whitening as a method of combating hyperpigmentation consists of two main elements:
- exfoliation of the stratum corneum;
- reduction of melanin production (specific depigmentation therapy).
For exfoliation, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) are most often used, such as glycolic, lactic, citric, etc. Exfoliation of age spots can also be carried out using hardware methods (laser resurfacing, dermabrasion). The purpose of such procedures is to exfoliate dead cells from the surface of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, and at the same time remove surface pigmentation.
Whitening products that reduce melanin production
To reduce melanin production, the following are usually used:
- substances that reversibly inhibit melanin synthesis in melanocytes (hydroquinone, azelaic acid);
- tyrosinase enzyme inhibitors (arbutin, kojic acid);
- derivatives of ascorbic acid (magnesium ascorbyl-2-phosphate).
In addition, the production of melanin is reduced by substances that bind divalent metal ions necessary for the synthesis of melanin (copper, zinc, iron), anti-inflammatory drugs, and antioxidants.
None of the listed effective skin whitening products are absolutely safe and therefore do not fit the definition of cosmetics that are used widely and uncontrolled.
Hydroquinone is very toxic. Kojic acid and arbutin are more gentle substances. Despite its toxicity, hydroquinone is still used in modern medications because it provides an obvious therapeutic effect.
It should be remembered that it is impossible to get rid of age spots in one session. The full course takes at least 60 days: pigmented cells are gradually removed from the surface of the skin, and new ones, devoid of pigment, take their place.
In addition to salon procedures, for a successful clinical result, home care is required: in the morning and evening, drugs with the active substances listed above are used.
Hyper- and hypopigmentation of the skin
Pigmentation is the coloring of human skin a certain color. If a person is healthy, his skin will have a natural color. When disease or injury occurs, the skin may change color, becoming darker (hyperpigmentation) or lighter (hypopigmentation).
Hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is caused by an increase in the amount of melanin, the substance responsible for coloring the skin (pigment). Pregnancy or certain diseases, such as Edison's disease (adrenal gland dysfunction), can provoke increased melanin production and hyperpigmentation. Exposure to sunlight is the main cause of hyperpigmentation and even further darkening of the affected areas of the skin.
Hyperpigmentation can also occur under the influence of various medications, including some antibiotics, antiarrhythmics, and antimalarials.
Melanosis of the skin
An example of hyperpigmentation is a condition called cutaneous melanosis or chloasma. It is characterized by the appearance, most often on the face, of brown and yellow-brown spots. Melanosis can appear in pregnant women, in which case it is often called the “mask of pregnant women,” but not only women, but also men suffer from this disease. In pregnant women, melanosis stops after childbirth. It can also be treated with certain prescription creams (such as hydroquinone).
If you have melasma, try to limit your exposure to the sun. Always use a strong sunscreen (SPF 15 or higher), as sun rays can worsen the skin of a person with melanosis. Sunscreens containing zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and Parsol 1789 (avobenzone) protect the skin best.
Before independently choosing one or another type of treatment for melanosis, be sure to consult with your doctor.
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is the result of decreased melanin production. Examples of hypopigmentation are:
- Vitiligo .
This disease causes smooth, discolored patches of skin to appear. For some people, these spots may cover the entire body. This is an autoimmune disorder that destroys the cells that produce pigment. Vitiligo cannot be completely eliminated, but there are several ways to treat the condition, such as cosmetic concealers, corticosteroid creams, and light therapy. - Albinism.
This is an inherited disorder caused by a lack of the enzyme that produces melanin, resulting in a lack of pigmentation in the skin, hair and eyes. Leukopathies have an abnormal gene that prevents the body from producing melanin. A complete cure for albinism is impossible. People suffering from this condition should constantly use sunscreen as they are the most susceptible to sunburn and skin cancer. Albinism can develop in people of any race, but it often affects fair-skinned people.
- Loss of pigmentation as a result of skin damage.
If you have had a skin infection, blistering, burns, or other trauma to the skin, the damaged area may become discolored. Most often, the loss of pigmentation that occurs as a result of skin damage is a temporary phenomenon, but the recovery period takes a fairly long period. Until the pigment is restored, special cosmetics can be applied to the discolored areas of the skin.
The materials were prepared by doctors from the Department of Dermatology at the Cleveland Clinic.
Existing types and classification
The following types of hyperpigmentation are distinguished:
- primary;
- secondary;
- generalized (widespread).
The primary ones include:
- freckles;
- melasma;
- lentigo;
- Becker's nevus;
- photodermatoses;
- melasma.
Secondary formations occur after:
- chronic acne (acne);
- laser destruction;
- hypermelanosis (against the background of hair loss).
Common ones provoke:
- chronic intoxication of the body;
- deficiency of vitamin B 12;
- Addison's disease;
- pathologies of the liver and adrenal glands.
Fitzpatrick scale of skin color and melanin production
Preventive measures
Preventive measures include:
- reducing the time the epidermis is exposed to direct sunlight, as well as avoiding visiting a solarium;
- use of high-quality cosmetics;
- to give up smoking;
- caution when using natural essential oils;
- timely treatment of inflammatory dermatological diseases, as well as other third-party spots, neoplasms, and so on;
- refusal to independently remove extensive acne;
- limiting the use of peelings and scrubs, especially before going outside in sunny weather.