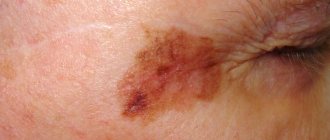
Melasma is an acquired benign disorder of skin pigmentation, locally limited, developing to a greater extent in the face and neck. Melasma appears unevenly in the form of spots on the skin ranging from light brown to dark, black. Melasma spots have clear contours and are mainly located on open areas of the skin. Melasma does not affect the mucous membranes. Pigment spots with melasma do not peel off, the structure of the affected areas of the skin does not change. Melasma tends to lighten in color during the fall and winter months. During the spring-summer period of active sun, melasma acquires a brighter shade. Women are more often affected by melasma. In men, this type of hyperpigmentation is extremely rare, which is due to the hormonal etiology of this disease. Melasma can manifest itself as single lesions of the skin, or as many spots over the entire exposed surface of the skin (face, neck, décolleté, hands).
Types of Melasma
There are three classifications of melasma based on clinical, histological features and the nature of the disease.
Thus, according to clinical signs (based on the localization of manifestations of age spots), melasma is divided into three main types:
- Painting - the main foci of skin lesions are localized in the cheeks and nose;
- Central facial (centrofacial) – pigment spots are localized in the forehead, nose, upper lip, chin;
- Mandibular – spots of melasma affect the arch of the lower jaw.
According to the nature of the disease, melasma is divided into:
- Passing - the spots are temporary and disappear completely after the cessation of exposure to the factor that stimulates the production of melanin and the development of age spots (hormones, sun rays);
- Persistent - melasma that changes from a more severe to a lighter form, but does not go away completely.
Based on histological characteristics, they are distinguished:
- Epidermal melasma is an increase in the amount of melanin in the layers of the epidermis. The light brown hue of melasma spots becomes brighter under a Wood's lamp;
- Dermal melasma is an increase in the amount of melanin in the superficial and deep layers of the dermis. This pathology is characterized by spots of an ashen or bluish-gray hue. Pigmentation does not become brighter under Wood's lamp;
- Mixed melasma - this pathology is characterized by damage to both the superficial epidermal layers and the deep layers of the dermis. Melasma spots of this origin are usually dark brown in color and do not change under a Wood's lamp.
Melasma and chloasma - is there a difference?
There is no definite opinion among scientists regarding whether these concepts are synonyms of one disease or not. The difference in definition lies in the causes of hyperpigmentation. That is why the concepts of “Melasma” and “Chloasma” are somewhat different.
- Melasma is a broader concept that does not include the cause of its occurrence.
- Chloasma is a simplified manifestation of melasma, which is a pathological hyperpigmentation caused by pregnancy. The second concept is popular among European dermatologists.
The occurrence of chloasma is a consequence of the following disorders:
- the amount of melanin production is exceeded;
- hormonal disbalance;
- diseases of the reproductive system;
- diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract.
There are specialists who separate the two concepts, taking into account the areas of damage and the nature of the localization of pigmentation. Practice indicates the same type of manifestation, treatment methods, and prevention methods, which allows these two concepts to be equated.
Reasons for the development of melasma
The main factors determining the appearance and development of melasma are:
- Ultraviolet radiation – UV rays stimulate the production of melanin (melanogenesis), as well as the proliferation of melanocytes (skin cells responsible for the production of melanin pigment);
- Genetic predisposition;
- Gender;
- Hormonal imbalance (taking hormonal contraceptives, pregnancy, ovarian dysfunction);
- Impaired liver and thyroid function;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Therapy with photosensitizing drugs (stimulating increased skin sensitivity to ultraviolet rays);
- Disruption of the body's metabolic processes, provoked by an excess or deficiency of minerals and vitamins;
- The use of certain cosmetics.
Melasma, chloasma
What aesthetic defects can be called the most unpleasant? Perhaps those located in open areas of the body are obvious to others and at the same time extremely difficult to correct.
Melasma (chloasma) is one of the most common types of skin pigmentation. Classified as a benign formation, it consists of brown spots of various colors - from light to almost black - of a small area, located mainly in the area of the bridge of the nose, forehead, cheeks and above the upper lip.
According to medical statistics, women are most susceptible to this disease - only 5% of the total number of cases are among the stronger sex. Most often, spots appear between the ages of 20 and 50, and people with dark skin and a good reaction to tanning (under the sun or in a solarium) are at particular risk.
The most unpleasant thing for those faced with this type of hyperpigmentation is the fact that it is extremely difficult to treat. Only every third patient manages to completely get rid of melasma; in other cases, it is possible to only temporarily lighten the spot, after which an inevitable relapse occurs after a few months.
↑ Melasma and chloasma - what's the difference?
These words are often used as synonyms - which is quite justified in the context of treating symptoms, since in both cases they are absolutely the same. And even in the medical community there is no consensus on whether we are talking about one pathology or two different ones. Among supporters of the distinction there are two main approaches:
- The first is based on the causes of pigmentation: chloasma is considered to be associated with hormonal imbalances, diseases of the reproductive system or liver, melasma is considered as a consequence of problems with the gastrointestinal tract or general problems with pigment formation.
- The second (especially common among Western specialists) is essentially a simplified version of the first - chloasma here refers to melasma that occurs during pregnancy. In English, there is even a stable phrase “mask of pregnancy” to denote it.
In the context of this review, we will use melasma and chloasma interchangeably, since we are talking primarily not about medical theory, but about specific treatment and prevention techniques that are common to them.
↑ Causes of melasma
The appearance of dark spots on the skin is the result of increased activity of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes). A variety of factors can stimulate this activity:
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the skin - prolonged exposure to the open sun, visiting a solarium beyond reasonable limits. UV rays stimulate the production of melanin and the proliferation of melanocytes
- Hereditary predisposition to hyperpigmentation, i.e. melanocytes are extremely sensitive and susceptible to any irritants
- Various hormonal disorders: ovarian dysfunction, disorders of the liver, thyroid gland, pregnancy, taking hormonal contraceptives (at the same time, it is known that taking hormonal drugs as part of replacement therapy for menopause does not lead to such consequences)
- Using/taking cosmetics and medications containing photosensitizers - substances that increase skin sensitivity to sunlight
- Gastrointestinal diseases and metabolic disorders in the body due to excess or deficiency of essential vitamins and minerals.
| Photo 1 – what melasma (chloasma) looks like: | |
It is worth noting that not too much scientific research has been carried out on this topic, so it is not always possible to talk about a strict cause-and-effect relationship between one or another internal problem of the body and the appearance of spots, but in each of the above cases the risk of encountering them increases significantly.
↑ Types of melasma
Benign hyperpigmentation of the skin on the face is classified on several grounds. First of all, depending on the depth of occurrence in the skin:
- Epidermal . In this case, the spots are located in the epidermis, have a light tone and clear boundaries, which are easily determined in the rays of an ultraviolet lamp. This type of melasma is treated more successfully than all others;
- Dermal . The pigment is produced throughout the dermis, the contours of the spots are blurry, and the color is dark brown. Most difficult to treat;
- Mixed . Heterogeneous spots of various tones and varying degrees of clarity. Corrected with varying success - usually in this case, some areas of the skin respond to treatment better than others.
Depending on the nature of the disease, melasma/chloasma can be:
- Passing . Some time after eliminating the main factor that caused the production of melanin in the skin, age spots completely disappear;
- Persistent . Over time, the spots become smaller and lighter, but do not go away completely.
| Photo 2 – melasma on different areas of the facial skin: | |
Sometimes all pigment formations in people with initially dark, almost black skin are identified as a separate type, which does not have its own name. In particular, in the USA, where the percentage of such patients is much higher than in Russia, some dermatologists and cosmetologists specialize exclusively in working with them. The main problem is that it is impossible to use laser and photo techniques in this case due to the large number of side effects.
↑ Treatment of melasma and chloasma
To successfully get rid of pigmentation, you first need to accurately determine the cause of the appearance of spots on the skin. This group of diseases is dealt with by dermatologists or dermatovenerologists with the involvement of additional specialists, depending on the identified causes. It only makes sense to contact a cosmetologist to lighten spots, which does not exclude the need for full treatment.
Chloasma, caused by pregnancy and the associated hormonal changes, is highly likely to disappear on its own after childbirth and the end of the breastfeeding period. In other cases, you should be prepared for a long process of diagnosing and eliminating the internal factors that caused pigmentation.
In parallel with the main treatment, cosmetic whitening procedures can also be carried out. Since the spots do not cause pain and do not threaten health, the issue of skin lightening remains at the discretion of the patient; however, treatment is almost always sought precisely for the sake of an aesthetic rather than a therapeutic result.
It is important to understand here that for today’s cosmetology, complete removal of melasma and chloasma is an almost impossible task , no matter what numerous advertising texts say on this topic. It is possible to successfully even out skin tone in approximately 30% of cases, but there is a very high probability of relapse after prolonged contact with UV rays or any hormonal fluctuations. Let's look at the main methods:
- Various types of peelings. As a rule, this is laser or chemical peeling, less often microdermabrasion. The point is to remove the top layer of skin, along with which shallow spots are also “removed”. Ineffective for dermal melasma (theoretically, part of the dermis can be removed, but in this case a scar is guaranteed to remain).
| Photo 3 - before and after treatment of melasma (combination of superficial chemical peeling with a course of external preparations based on hydroquinone): | |
- Correction with fractional or neodymium laser. Allows you to reach melanin in the deeper layers of the skin. Fractional - more traumatic for surrounding tissues, neodymium - practically does not affect them. Currently the most common treatment option.
In 2014, at the IMCAS conference, the central international event for aesthetic surgery, cosmetology and dermatology, the President of the European Association of Laser Therapy in Dermatology (ESLD), Dr. Moshe Lapidot, summarized scientific research data related to the treatment of melasma with laser.
The specialist’s conclusions are as follows: 6 months after completion of the procedures, their results were, at best, similar to the results of patients who used exclusively external sunscreens; at worst, there was a complete return of pigment. The most pronounced effect was obtained by patients who combined laser with cosmeceuticals.
Thus, it can be stated that modern laser techniques for working with melasma/chloasma can temporarily lighten spots, but in the long term they give practically no results. However, these procedures provide some benefit as part of complex therapy, enhancing the effect of whitening creams.
| Photo 4 – before and after treatment of melasma with fractional laser: | |
- Photo correction. This technique is essentially similar to laser, but here the pigment is destroyed by targeted high-density light pulses. The result is almost the same, but is considered a little more traumatic. It should be remembered that laser and photo correction can lead to increased pigmentation in the treated areas under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, so the skin after these procedures must be especially carefully protected from the sun.
- Mesotherapy. Injection into the problem area of the skin of specially formulated cocktails (the main ingredients are ascorbic, glycolic, phytic and other acids), which suppress the activity of melanocytes and contribute to the destruction of pigment. Typically used in combination with peelings.
- External skin lightening agents. Compared to most salon treatments, creams, serums and masks from whitening cosmeceutical lines work surprisingly well: the result does not appear immediately, but remains very lasting in the long term. Particular attention should be paid to products that contain hydroquinone - it was this substance and its derivatives that were named the best helpers in the fight against annoying stains at the same IMCAS-2014.
| Photo 5 – melasma before and after a course of whitening cosmeceuticals (NuDerm system, Obagi): | |
In general, in the case of melasma, an integrated approach is more relevant than ever - by combining different types of procedures (of course, under the guidance of one cosmetologist responsible for the entire course of treatment), you can achieve much more pronounced results than by focusing on just one thing.
| Basic procedures for removing hyperpigmentation of the melasma / chloasma type: | ||
| Methodology | What's the point? | Peculiarities |
| Various types of peelings | The top layer of skin is removed, incl. and melanin stained areas | Allows you to get rid of epidermal melasma only |
| Laser and photo correction | Resolution of melanin with directed laser energy or pulsed color | You can work with deep layers of skin. The initial effect is good, but within a few months the pigmentation is restored in full or partial volume |
| Mesotherapy | Superficial injections of drugs that destroy melanin and suppress the activity of melanocytes | The effectiveness is average, works optimally in combination with peelings |
| Whitening cosmeceuticals | Products for external use, the principle of action is similar to mesotherapy | To achieve visible results, it will take from 3 to 9-12 months of regular use. The most effective component of such products - hydroquinone - can cause allergies and inflammatory processes in the skin |
↑ Prevention of melasma
To reduce the risk of age spots, as well as to consolidate successful treatment results, experts recommend paying attention to the following points:
- If you are prone to skin hyperpigmentation, you should avoid using hormonal contraceptives or select them with special care and only after consulting your doctor;
- At any time of the year, apply cosmetics with an appropriate broad-spectrum protective factor against ultraviolet radiation to exposed skin, especially the face;
- Avoid taking medications, foods and dietary supplements that contain substances with photosensitizing properties (and there are several hundred of them);
- You should regularly moisturize your facial skin and refrain from using aggressive cosmetics to cleanse it;
- Cosmetics containing α- and β-hydroxy acids (AHA, BHA), retinoids and other whitening substances can only be used after consultation with a dermatologist.
Diagnosis of melasma
Melasma is manifested by only one clinical symptom - a group of clearly defined spots on a certain (usually open) area of the skin. When diagnosing a pathological change, in order to select the correct treatment tactics, melasma must be differentiated from such disorders that have similar symptoms and external manifestations, such as:
- Secondary hyperpigmentation;
- Xeroderma pigmentosum;
- Poikilodermic lymphoma of the skin;
- Riehl's melanosis;
- Nevi.
The main method for diagnosing melasma is the Wood's lamp, which allows the classification of melasma.
Hyperpigmentation: types and symptoms
Abnormal pigment formation on the skin can be congenital or acquired. The localization of pigments can also be different, generalized (widespread) and local: hyperpigmentation appears on the face, back, arms and other parts of the body.
What types of enhanced pigmentation are there and how are they characterized?
- Freckles (small spots of different colors) are a congenital pigmentation: they can be located only in one area (for example, the face) or cover a large area (the back, arms or the whole body).
- Birthmarks (congenital pigmentation) can be of different sizes and shapes and “choose” different locations; they can change or remain unchanged during a person’s life.
Acquired hyperpigmentation includes the following types:
- diffuse melasma, which manifests itself in the form of spots of a brown or bronze hue and is located on open areas of the body, as well as near the nipple areolas, in the perineum or along the white line of the abdomen;
- arsenic melasma, which appears after treatment with arsenic products, spreads throughout the limbs, sometimes throughout the body;
- focal (in the oral cavity) and generalized melasma;
- melasma appears after too long exposure to the sun, in the form of spots of different shapes and colors;
- chloasma refers to pigmentation, which more often appears as a result of hormonal changes in the form of spots with clear boundaries (the main location is the face);
- lentigo is called age-related pigmentation that appears naturally;
- pigmentary toxicerma, limited pigmentation of the forehead and Broca's pigmented perioral dermatosis, etc.
Skin pigmentation should not be ignored, since (as stated above) any pathology can be not only a consequence of some external influence, but also a symptom of some general disease
For any changes in pigment, you should consult a doctor, at least for your own peace of mind, to make sure that everything is fine and there is nothing to worry about. If pigmentation is a signal of disturbances in the functioning of the body, then a timely visit to the doctor is an opportunity to take care of your health in a timely manner.
Melasma: treatment, basic methods
Melasma is characterized by resistance to various treatment methods. It should be remembered that melasma is a kind of reaction of the body to an irritating factor (excessive radiation, hormonal therapy). For melasma, treatment will be ineffective without eliminating the provoking factor. With a passing form of melasma, symptomatic treatment is prescribed, aimed at reducing the manifestations of age spots.
The main treatments for melasma are:
- Drug therapy is the use of topical drugs, the action of which is aimed at inhibiting and inhibiting tyrosinase (an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of melanin from tyrosine). The main side effects of topical medications for the treatment of melasma are secondary hyperpigmentation, dermatitis, erythema, and burning. This technique is most effective for the treatment of epidermal melasma;
- Injection methods – intradermal administration of drugs that inhibit tyrosinase;
- Hardware treatment – the use of light methods (lasers, intensely pulsating units). This method of treating melasma allows you to selectively act on the melanin contained in pigmented cells, without affecting the surrounding healthy cells. Laser correction of age spots involves the destruction of micro areas of the skin, in place of which healthy cells with normal pigmentation then develop. The main disadvantage of the technique is the increased risk of developing post-traumatic pigmentation of the treated skin areas. For epidermal and dermal forms of melasma, treatment with hardware techniques is the most effective;
- Chemical peels – removal of the top layer of the epidermis in order to restore the skin regeneration process and inhibit the processes of melanogenesis. To correct age spots, superficial and medium peels are used. The use of deep aggressive peeling techniques for the treatment of melasma is not justified, since the effectiveness of the technique is low compared to the risk of developing secondary hyperpigmentation.
Causes of chloasma
The appearance of melasma is the result of high activity of melanocytes - cells that produce the pigment melanin. The reasons for this increased activity of melanocytes may be the following:
In many cases, hyperpigmentation spots are localized on the face.
This disease is characterized by the appearance of flat, irregularly shaped spots, the color of which can vary from light to dark brown, depending on the severity of hyperpigmentation.
Melasma is most often localized on open areas of the body (face, neck, décolleté, hands). In the autumn-winter period, the intensity of the color of the spots may decrease, and in the spring and summer, when solar activity increases, the affected areas may become darker, since melanin production increases under the influence of UV rays.
The development of chloasma can be triggered by many reasons or a combination of them. The most common factor is a hormonal imbalance that occurs during puberty or while pregnant.
The cause of the disease can be diseases of the genitourinary system - adnexitis, endometritis, salpingitis, inflammation of the bladder, etc.
Hyperpigmentation of the skin is also caused by disruption of the functioning of internal organs. In particular, chloasma is provoked by liver disease and biliary tract dysfunction.
Often the cause of the pathology is diseases of the central nervous system. First of all, this is encephalitis; less often, tumor formations of a malignant or benign nature can provoke the disease.
Chloasma can be caused by diseases of the digestive system, in particular those accompanied by maldigestion or malabsorption. In addition, severe intoxication of the body, previous tuberculosis or malaria can be a provoking factor.
Other causes of chloasma include:
- hypovitaminosis and vitamin deficiency (hyperpigmentation is especially pronounced with a deficiency of vitamin B9 and ascorbic acid);
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays on the skin (including in a solarium);
- the effect of aggressive chemicals on the epidermis;
- frequent use of cosmetics containing essential oils.
Today, modern dermatology is not able to name the exact causes of the development of chloasma. Most scientists studying this phenomenon agree that excessive melanin deposition, which causes the development of chloasma, occurs due to the presence of various metabolic and endocrine disorders in the body.
This point of view is confirmed by the frequent diagnosis of chloasma in people with chronic liver diseases (liver cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, viral hepatitis), in women during pregnancy and with various inflammatory gynecological diseases (Endometritis, Oophoritis, Salpingitis, Adnexitis).
Melasma: treatment with Skinoren
When diagnosing melasma, treatment with Skinoren is one of the most effective methods currently used. Skinoren is a dermatoprotective agent for external use, which has a depigmenting, antibacterial, keratolytic, and anti-inflammatory effect. The main active ingredient in the drug is azelaic acid, which has an effect on hyperactive melanocytes due to the inhibition of tyrosinase. For melasma, treatment with Skinoren is most effective in the early stages of the disease. Skinoren is available in cream and gel forms with varying concentrations of the active substance. For melasma, treatment with Skinoren involves a course lasting 3 months. The main side effects of Skinoren are hyperemia, burning, itching. Skinoren is effective for epidermal melasma. Dermal melasma cannot be treated with this drug.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Features of therapeutic treatment of chloasma/melasma
Therapeutic treatment of pathology should be carried out by a dermatologist. Initially, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound diagnosis of the genital organs, take hormonal tests, and obtain a gynecologist's opinion.
After this, the dermatologist must conduct tests for tumor markers to exclude the malignant nature of the pathology.
Therapeutic treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause - the individual factor that became the impetus for the appearance of pigmentation.
The standard correction scheme provides:
- complete abolition of hormonal contraceptives (provided that they were taken by the patient);
- a ban on taking medications, food and using cosmetics that have a photosensitizing effect;
- mandatory year-round use of sunscreen compounds;
- exclusion of independent use (without the prescription of a specialist) of products based on retinoids, alpha and beta hydroxy acids;
- the use of soft compositions for cleansing the skin with a neutral ph level;
- taking topical corticosteroids, which show positive results in the treatment of pigmentation directly related to inflammatory processes occurring in the skin. They should not be used during pregnancy;
- oral intake of special supplements that contain vitamin C, Omega 3 unsaturated fatty acids, oligomeric proanthocyanidins, condensed tannins, leukoanthocyanins, which have an antioxidant effect.