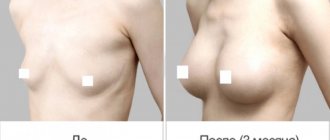
Causes
The causes of this complication may be:
- The body's reaction to an endoprosthesis. A prosthesis for a woman’s body is a foreign body that can be rejected. The implants are made of biological material, so the likelihood of rejection is very low and passes quickly. But there is always a percentage of women who are sensitive to biological material, which may increase the risk of fluid accumulation after surgery. But modern surgery cannot yet determine the body’s reaction to the implant before surgery;
- Damage to lymphatic vessels. This cause of fluid accumulation in the chest occurs when blood vessels are damaged during surgery. The vessels are restored during the first day after the operation, but sometimes this process slows down, which leads to the release of lymph;
- Bleeding tissue. During surgery, small capillaries tend to leak into the soft tissue of the breast and form a serous substance at the site of implant installation;
- Presence of hematoma . When the resorption of the hematoma begins, accumulations of ichorous substances form and the formation of a seroma. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the patient for several days after the operation;
- Lack of normal drainage . Any operation, like mammoplasty, is accompanied by the release of lymph, and if it is not removed in time, this provokes complications;
- The body's reaction to suture material . In modern surgery there are a lot of high-quality surgical materials, but none of them are ideal. Also, with a large use of absorbable threads, they lead to accumulation of substances.
Photo: Seroma
The main factors and causes of the formation of the disease
Serous fluid after surgery is an abnormal concentration of moisture formed due to a violation of the integrity of blood vessels during surgical manipulation of soft tissues. It is a liquid substance of a straw-yellow hue, with a strong sweetish odor, especially when it penetrates through an incision suture or fistula. In this case, the degree of viscosity depends on the amount of proteins and lipids, and the red tint depends on the red blood cells.
The liquid contains:
- Leukocytes.
- Lymphocytes.
- Macrophages.
- Squirrels.
- Lipids.
- Red blood cells.
According to the ICD 10 classification scheme, seroma after breast surgery does not have an individual code. It is diagnosed based on the type of surgery performed and the provoking factor that led to the complication. In most cases, pathology develops after:
- Abdominal plastic surgery.
- Caesarean section.
- Mastectomies.
The ICD surgical code 10″O 86.0″ means the presence of purulent wounds in the postoperative cavity.
Seroma after mammoplasty is a rather rare occurrence (observed in 1% of women undergoing surgery), however, if you suspect it, you should immediately contact a specialist, be sure to indicate the exact time and day of the onset of its first symptoms.
Main provoking factors:
- Injury to lymphatic and venous vessels, and leakage of lymph into the tissue.
- May be a consequence of hematoma after mammoplasty.
- Lack of adequate drainage, which is a primary condition for any operation.
- Individual allergy of the body to implants and suture material.
- Increased threshold for bleeding (small capillaries during plastic surgery enter the tissue, creating a liquid mass in the area where the implant is implanted).
- Insufficient professionalism of the surgeon.
- Failure of the patient to comply with medical recommendations.
Complications can be caused by:
- Diabetes.
- Overweight.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Age.
Surgery considers the presence of seroma a dangerous anomaly, since a gradual increase in exudate can lead to irreversible consequences.
Signs of disease development
The first symptoms of complications begin to be observed 4-14 days after surgery. However, it should not be confused with ordinary swelling, which disappears on its own.
Seroma of a postoperative scar in the chest is manifested by the following clinic:
- Deformation and enlargement of the female breast; in some cases, the nipple is displaced; upon palpation, a lump is felt, and the skin at its location becomes stretched.
- Development of severe edema. The thick serous substance is not limited to any bladder (shell), and therefore is able to penetrate all soft tissues.
- Rapid rise in temperature.
- Swelling in the operation area.
- Constant pain discomfort indicates the accumulation of a large amount of fluid.
- When you press on the scar, moisture appears.
- The wound area takes on a rich, bright red color.
Regardless of any signs, you should never self-diagnose gray; only a specialist can confirm its presence.
What complications are seroma dangerous for?
A long-term absence of appropriate treatment for seroma can lead to the appearance of a fistula tunnel. The presence of a fistula is more often observed in patients with soft and thin skin; in addition, those women who have enlarged their breasts several times are at risk, thereby causing excessive skin tension.
Ignoring the presence of seroma provokes the development of:
- Capsular contracture.
- Fistula.
- Suppuration.
- Tissue necrosis.
In the clinic described above, the question of repeating the operation is considered in order to eliminate the implant and excise dead tissue.
The opinion that seroma can resolve on its own without therapy and preventive steps is a huge mistake. In some episodes, such a clinic was observed, but there is always the possibility of an increase in the amount of fluid that is not capable of disappearing on its own.
Factors
The accumulation of serous material after mammoplasty appears within 5-7 days after surgery.
One of the significant signs influencing the accumulation of fluid in the breast is a mastectomy (removal of the mammary gland), which increases the appearance of lymph nodes.
Another factor contributing to the appearance of serum may be inflammatory processes in places of skin injury.
There may also be factors such as:
- diabetes;
- excess weight. Greater thickness of subcutaneous fat increases the risk of fluid appearance;
- increased blood pressure;
- age.
Treatment of seroma after breast surgery
Every year, more and more women turn to surgeons to perform breast augmentation or plastic surgery operations.
But not every representative of the fairer sex knows about the possible appearance of seroma after breast surgery. Statistics show that seroma occurs in 15% of patients who have undergone breast surgery.
Seroma is a complication caused by surgical intervention, manifested by the accumulation of serous fluid. With this pathology, fluid accumulates inside the mammary gland, which stretches it. A woman's breasts sag.
Symptoms of seroma after mammoplasty
Do not forget that seroma appears in many women after breast correction, so it is worth consulting a specialist and monitoring the healing process and, of course, paying attention to the symptoms of fluid manifestation for its timely prevention and treatment.
The main symptoms of fluid accumulation may be:
- change in breast shape . The breast increases in volume, a lump may appear in the place where fluid is collected, the contour changes and the nipple moves.
- soft tissue swelling. Since the liquid does not remain outside the capsule, it has the ability to penetrate into soft tissues and when palpated, a certain elasticity and tension of the skin can be felt;
- pain in the area of fluid accumulation . Usually the pain is normal and moderate, but with pressure the pain intensifies. Pain can also be felt during physical activity and walking;
- redness of the skin in the seroma area . This symptom is explained by the fact that the liquid exerts pressure and destroys small vessels, and therefore the color in the area of accumulation may change;
- discharge of serous matter through the edges of the wound. This symptom occurs extremely rarely, but if such a complication persists for a long time, then an outlet may form - a “fistula”, through which the substance will come out. This complication is typical for patients with thin skin.
After breast augmentation, a patient notices that the breasts are enlarged, swelling appears, which increases every day, redness appears in the area where the substance accumulates, and pain becomes more frequent.
Postoperative suture seroma after cesarean section
Complications in women whose obstetrics were performed by caesarean section are common. One of the reasons for this phenomenon is the mother’s body, weakened by pregnancy, which is unable to ensure rapid regeneration of damaged tissues. In addition to seroma, a ligature fistula or keloid scar may occur, and in the worst case scenario, suppuration of the suture or sepsis. Seroma in women giving birth after a cesarean section is characterized by the fact that a small dense ball with exudate (lymph) inside appears on the suture. The reason for this is damaged blood vessels at the site of the incision. As a rule, it does not cause concern. Seroma of postoperative suture after cesarean does not require treatment.
The only thing a woman can do at home is to treat the scar with rosehip or sea buckthorn oil to speed up its healing.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis methods for complications include:
- ultrasonography;
- x-ray mammography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Using ultrasound, you can determine the internal changes occurring in the breast area after mammoplasty, determine the degree of seroma development and diagnose it in the early stages of formation.
X-ray mammography is indicated for all women who have ever undergone breast surgery, as well as women over 40 years of age.
This research method helps to assess the nature of the condition of the mammary glands and helps determine the nature of the formation of nodes, compactions and the formation of fluids in the breast area.
Unlike X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging involves the absence of radiation exposure and diagnosis is carried out for each case separately.
Magnetic resonance imaging will help monitor the condition of implants after mammoplasty, and also help prevent the development of complications such as seroma and contracture.
Treatment options
Such a formation in the breast as a gray tumor can be treated using two methods, such as surgery and medication. Large lesions can be treated simultaneously in two ways.
The surgical method is accompanied by the presence of adequate drainage.
A drain is installed to remove serous fluid and can be left in place for two to three days. Based on the amount of substance released, a specialist can judge whether the drainage should be removed or not.
Drainage is a fairly popular method of treatment, in which the process of removing the discharged substance from places of accumulation occurs.
Special devices can be removed from the wound, but generally, specialists remove fluid through special punctures located around the wounds.
The skin that is located near the installation site of the drainage system must be wiped with a solution of brilliant green.
Before starting the drainage procedure, all devices must be sterile and treated with sodium chloride in a proportion of 0.9%.
The medical worker must monitor the operation of the drainage system; if the tube falls out, it must be replaced with a new one. Only a professional should remove the drainage system.
Another method of treating seroma is vacuum aspiration. When carrying out this method, serous matter is suctioned from the site of accumulation of serous matter or postoperative wounds.
This method of treatment is used most often in the early postoperative period and ensures rapid healing of postoperative wounds.
The drug treatment method involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs and broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Find out whether you need to change implants after mammoplasty.
Why does a burning sensation appear in the breast after mammoplasty? The answer is here.
If the formation of fluid is small, then you should only take medications.
What is it - postoperative suture seroma?
We all know that many surgeons perform “miracles” in the operating room, literally bringing a person back from the other world. But, unfortunately, not all doctors conscientiously perform their actions during the operation. There are cases when they forget cotton swabs in the patient’s body and do not fully ensure sterility. As a result, in the operated person, the suture becomes inflamed, begins to fester or separate.
However, there are situations where problems with a stitch have nothing to do with medical negligence. That is, even if 100% sterility is observed during the operation, the patient suddenly accumulates liquid in the incision area that looks like ichor, or pus of a not very thick consistency. In such cases, they speak of seroma of the postoperative suture. What it is, in a nutshell, can be said this way: it is the formation of a cavity in the subcutaneous tissue in which serous effusion accumulates. Its consistency can vary from liquid to viscous, the color is usually straw-yellow, sometimes supplemented with blood streaks.
Dangers
A very big mistake is the statement that seroma will resolve itself without additional treatment and prevention.
In most cases, this may be true, but there is always a risk of an increase in the volume of fluid, which on its own cannot disappear and resolve.
This leads to subsequent complications such as:
- Formation of a serous fistula . In this case, the serous substance independently seeps through the soft tissue. Most often these are the edges of the wound. Such leakage can last up to several weeks, which contributes to infection of the endoprosthesis, which entails a repeat operation;
- Development of capsular contracture. The accumulation of fluid accompanies inflammatory processes, which ultimately leads to an increase in excess tissue. In turn, such tissue promotes the development and formation of the capsule;
- Suppuration of the place where the implant is located. The serous substance is an ideal place for the accumulation and development of bacteria, which can lead to suppuration of the implantation pocket.
Prevention
The best solution to the problem of fluid accumulation is timely consultation with a doctor and prevention.
Conventionally, the prevention of fluid prevention can be divided into levels:
- Preoperative;
- Interoperational;
- Postoperative.
Preoperative prevention is:
- taking tests;
- consultation and selection of a plastic surgeon;
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- electrocardiogram;
- consultation with a gynecologist.
Interoperative prevention is directly related to the actions of the plastic surgeon and methods of performing plastic surgery, which include:
- correct choice of area for implant placement;
- adequate incision placement;
- timely wound drainage;
- high-quality sutures.
Postoperative prevention is directly related to the patient’s behavior during the rehabilitation period.
In the postoperative period, the patient must follow the following rules:
- wearing compression garments;
- attending all consultations and following all recommendations of the attending physician;
- restriction of physical activity and movement.
Photo: Compression underwear
Compliance with all preventive measures and careful attitude towards your health will give you a good aesthetic result after surgery and reduce the risk of complications after mammoplasty.
Prevention of the appearance of serous matter also includes the following actions:
- suturing the wound without leaving pockets;
- apply a pressure bandage to the wound area for several hours;
- constant use of antiseptics and antibiotics at all stages of treatment.
See what ripping looks like after mammoplasty.
Study the list of restrictions after mammoplasty in this article.
What is the cost of mammoplasty? Read more.