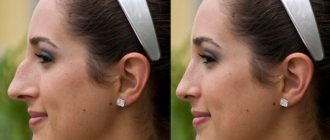- June 22, 2018
- Surgery
- Yulia Lobach
Intervention during surgery is very often associated with complications, including tissue hemorrhages and hematomas. Even without a medical education, it is easy to understand that during this process small blood vessels and capillaries can be damaged. Even the pressure of instruments on the edges of the wound when moving it apart can contribute to this.
Along with the existence of various reasons for the appearance of hematomas after surgery, there are many methods to combat them.
Causes
According to studies, during surgical interventions, eight out of a hundred patients develop hematomas as postoperative complications. Such bruises can appear from subcutaneous hemorrhage immediately after surgery, and sometimes they appear only after several days.
Hematoma after surgery can be caused by the following factors:
- high blood pressure in the period after surgery;
- insufficient blood clotting caused by any diseases or certain medications;
- manifestation of atherosclerosis;
- violation of the integrity of blood vessels;
- vascular diseases or injury;
- non-inflammatory (hemorrhagic) rash;
- the presence of persistent infection;
- very severe diseases of blood vessels and internal organs, such as neoplasms, cirrhosis of the liver and vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels);
- nutritional problems, lack of vitamins K, B, C and folic acid.
Postoperative
Postoperative hematomas
Postoperative hematomas are a very special type of hematoma. They can be of absolutely any type from the above classification: subcutaneous, cavitary, tense, and infected.
It is important to understand that most often such “bruises” are a normal stage of the postoperative period. This is not the fault of the surgeon, nor the suture material, nor postoperative care - these are only the individual characteristics of the patient himself, the nuances of the operation itself and the course of the postoperative period. Of course, there are factors that predispose to the development of bruises after surgery and medical procedures.
Features of operations. Operations performed on areas of the body with a pronounced vascular network and richly supplied blood organs - face, mammary glands, thyroid gland, as well as on the vessels themselves - for example, leg veins, pelvic vessels. That is, for example, a hematoma on the leg after surgery for varicose veins is a completely normal occurrence.
The patient is taking special medications that affect the coagulation system: Warfarin, low molecular weight heparins, antiplatelet agents. It is recommended to discontinue such drugs at least a month before the proposed operation, but this is not always possible due to the patient’s health. Arterial hypertension. This disease in a patient causes excess blood pressure in the vessels to push blood into the surrounding tissue, forming a bruise. Individual characteristics of the vascular wall and coagulation system, including the diseases listed above: thrombocytopenia, vasculitis and others.
Smoking. Smokers often have increased fragility of blood vessels and blood clotting characteristics, so the formation of bruises and post-operative bruises is much more common.
Drinking alcohol. Alcohol promotes vasospasm and increased blood pressure, which predisposes blood to leak from vessels that have not yet recovered into the surrounding tissue. Failure of the patient to comply with the doctor's recommendations. Early physical activity, improper dressings, and refusal to take medications can contribute to the formation of bruises and other postoperative complications.
Types of hematomas and their characteristics
We will consider the treatment of hematoma after surgery later, but for now we will determine their types. A hematoma is a hemorrhage into soft tissue that occurs when blood vessels are damaged.
In the process of cutting tissue, the surgeon can damage the numerous and branched vascular network, which will ultimately lead to hemorrhage. Its main indicators may be: painful sensations, a rapid change in skin tone, the appearance of swelling, and in the presence of internal hematomas, compression is felt, however, all these signs do not always appear and not immediately.
According to location, it is customary to divide hematomas after surgery into four types:
- hematomas located under the skin;
- between muscles;
- hematomas of the chest and abdominal cavity (cavitary);
- located inside the skull.
General concept
A hematoma on the skin appears as a bruise with swelling
A hematoma is an injury that manifests itself as a result of damage to the integrity of blood vessels and subcutaneous hemorrhage. Most often, soft tissues are damaged along with the vessels, resulting in swelling and severe pain.
On the surface of the skin, damage appears as a bruise and slight swelling. Sometimes, as a result of inflammation at the injury site, the temperature rises.
Depending on the location, the hematoma causes complications and side effects. For example, if the head is injured, swelling and bruising may spread to the neck and shoulders. This can even cause the palate to become numb and cause swelling on the tongue.
In addition to the external bruise, pain is felt, especially when pressed. Treatment of hematoma is determined individually, depending on the location of the injury and the degree of impact.
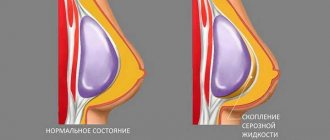
Subcutaneous hematoma
Subcutaneous postoperative hematoma refers to minor hemorrhage into the soft tissues under the skin. Blood may not penetrate the tissue, but rather collect in one place, resulting in the formation of a cavity. In this case, we can talk about a formation in the form of a bag.
Under the skin, a bruise is an oblong or round bruise. There are cases when, in the presence of numerous hematomas, hemorrhages form a cluster of spots.
One indicator is color change. First, red is replaced by purple, and then it becomes yellow-green. Before it disappears, the bruise looks like a brown spot, and remains like that for quite a long time, and leaves no trace behind. If a hematoma forms after an operation of this kind, you just need to wait.
Signs
Subcutaneous hematoma is the simplest type of bruise resulting from superficial injuries. Appears anywhere. As a rule, it has a round shape. At first it is red, then becomes purple, greenish-yellow and finally
brown. Accompanied by:
- local, sometimes throbbing pain;
- impaired muscle mobility;
- local inflammation.
Postoperative hematomas appear:
- in the abdominal region some time after removal of a hernia or appendix;
- on the breasts of women when they had a breast procedure;
- in the groin area in men, if they were treated with varicocele - dilation of the veins of the spermatic cord.
They are usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- distension;
- soreness;
- deformation;
- seals.
In this case, blood accumulates in the suture - it is removed by drainage in too large quantities. All this indicates that hemostasis was not performed very well.
Internal hematoma
This type of hematoma is an extremely dangerous form of hemorrhage, since in addition to damage to organs, large quantities of blood fill cavities or can accumulate between tissues.
In humans, these symptoms begin to appear with a sharp drop in blood pressure, the skin becomes pale, and pain appears at the site of the operation. Blood flows out through the drains in huge quantities. The condition is so dangerous that if the person is not put on the operating table at the right time and the bleeding vessel is not sutured, then everything can end sadly. For example, a hematoma after hernia surgery may be of this type.
When to see a doctor
Complications after implantation normally last 5-7 days. An alarming signal should be the persistence of unpleasant symptoms longer than this period. In this case, there is no need to postpone going to the doctor. Timely treatment will help avoid serious consequences.
You need to contact a specialist when you have:
- undiminished or growing swelling (normally, a decrease in the severity of edema, hematomas occur in the first days after implantation);
- acute, pulsating pain at the site of swelling;
- persistence of low-grade fever for 3 days, its increase;
- loss of sensitivity, numbness;
- the appearance of bad breath.
Opinion of an implant surgeon : “Although serious complications as a result of implantation do not occur often, the patient should carefully monitor his well-being. You can prevent the development of unpleasant consequences by timely and competently assessing the scale of the problem. If there is no positive dynamics, you should contact your dentist.”
Brain hematoma
Bleeding inside the skull can occur after injury or surgery. This phenomenon is deadly, as there is a possibility of irreversible damage to human brain tissue. Therefore, it is imperative to immediately diagnose and treat these cranial hematomas. The following types are distinguished:
- subdural, associated with traumatic brain injury;
- epidural;
- hematoma inside the brain.
The first hard shell is located between the brain and the bones of the skull. At the end of the operation, accumulated blood is found between this membrane and the skull. In medicine, this is called a subdural hematoma. Such conditions lead to increased pressure on the brain and changes in its functioning for the worse. There are cases when this type leads to death.
How to remove and alleviate the general condition
By following simple recommendations, you can get rid of the complications that have arisen or at least minimize their severity:
Dishes should have a puree-like consistency
- After the operation is completed, ice is applied to the site where the implant is installed for 15 minutes . At home, the patient must perform this procedure at least five times a day.
- The dentist applies dental paste to the wound to promote speedy healing and reduce discomfort.
- The patient should try to be in an upright position more often . At night, sleep on a high pillow to improve blood flow from the wound.
- Treat teeth located next to the implant with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- Rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic solution after eating disinfects and promotes healing of damaged mucous membranes.
- Avoid spicy, hard, or too hot foods.
- To relieve pain, you must take anti-inflammatory and painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
- Use heparin-based ointments to speed up the resorption of the hematoma.
- To brush your teeth, use a new, soft brush with natural bristles.
- Quit smoking for at least 2-3 weeks.
Treatment of hematoma after surgery
To treat the listed pathologies, a certain approach is required, and repeated surgery is not excluded. Treating these types of hematomas yourself is extremely dangerous. Under such conditions, the blood can quickly pick up an infection that penetrates from the surgical wound. A large hemorrhage can lead to extensive blood loss. Decomposition products can cause intoxication of the body.
The general danger is that:
- there is a risk of infection;
- a compaction appears at the site of the hematoma and does not disappear over time;
- the shape of the tissue changes, and the scars that appear in places of accumulation negatively affect their mobility.
When using modern laser surgery techniques, as well as the use of special instruments that can cauterize blood vessels in the wound during surgery, the risk of infection is reduced. We will talk further about in what cases anti-inflammatory ointments and other means of therapy are used.
After surgery, minor bruises will resolve on their own.
Applying cold helps stop bleeding as the blood vessels constrict. Applying a pressure bandage helps localize the leak on the arm or leg. Using a puncture and a syringe, the entire contents of the hemtoma are removed.
These methods are effective for superficial blood collection. A small incision, the so-called drainage, allows you to remove blood clots if the hematoma has coagulated or taken the shape of a bag.
Heparin-containing gels and anti-inflammatory ointments are excellent for treating skin with a small hematoma after surgery. They are applied to the bruise several times a day until the effect is completely gone. Physiotherapeutic procedures complement the treatment and help eliminate compaction and swelling.
For repeated prevention of hematomas, compression hosiery is used. A blood clot should form. And to achieve this effect, it is necessary to immobilize the limb. If bleeding is severe, the doctor will prescribe medications that increase blood clotting.
Bruises after rhinoplasty
Operations to change the size and shape of the nose are considered the most difficult to perform for a surgeon. And for the patient, the main problem is the recovery period, which is associated with a number of inconveniences and restrictions.
One of them is large bruises after rhinoplasty. They are formed due to damage to blood vessels and are usually located directly on the nose, around it, and under the eyes. This is not a complication, but an expected side effect that should go away on its own over time.
Is it possible to completely avoid the appearance of such hematomas and how long will it take to walk with them? Are there ointments or other products that will speed up resorption? Readers of Tecrussia.ru are advised by leading metropolitan plastic surgeons:
↑ Why is there no rhinoplasty without bruises?
To carry out the necessary manipulations, the surgeon peels off the soft tissues of the nose during the operation, and then, when the work is completed, returns them to their original position and applies sutures. Such actions always - even if the most modern, gentle techniques are used - injure the blood vessels, which leads to the appearance of characteristic swelling and subcutaneous hemorrhages on and around the nose.
If the patient has undergone an osteotomy (partial removal of bones), then bruises will also appear under the eyes. Also, sometimes blood gets under the cornea of the eye, such stains look like bright red spots on the whites.
- Swelling after rhinoplasty (stages of the process)
- Open and closed rhinoplasty – which option is better?
| The area around the eyes on the 2nd day after surgery: | |
↑ Are there any methods of prevention?
Unfortunately, it is not possible to completely avoid the appearance of hematomas. But ensuring that they are not frighteningly large and disappear quickly is quite possible:
- The most important factor here is choosing a good surgeon. How carefully a specialist works with his patient’s nose largely determines the size of future bruises.
- At least 2 weeks before rhinoplasty, you must stop taking any blood thinning medications (including aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.), and also stop drinking and smoking.
- At a young age (up to 30 years), the walls of our blood vessels are quite strong, they are more difficult to damage, and as a result, relatively small hematomas are formed. At the age of 40+, the walls become much more fragile, which leads to quite large subcutaneous hemorrhages. In addition, increased “fragility” of blood vessels can be inherited, so it is necessary to warn the surgeon if the patient himself or his relatives have already had cases of excessively large postoperative hematomas.
↑ Is it possible to speed up resorption?
Bruises associated with nose surgery are not dangerous to health and completely resolve within 2-3 weeks after surgery. In extremely rare cases, they last up to 4-5 weeks. Hemorrhages under the ocular cornea take much longer to resolve – up to 1.5 months.
| The same patient on the 7th day: | |
What can be done to reduce these deadlines? Immediately after surgery, when bruises are still forming:
- During the first 2-3 days, it is necessary to apply cold compresses to the forehead and areas under the eyes - for about 10-15 minutes every hour.
- For the same period, it is advisable to maintain an elevated position of the head during sleep (for this you need to place an additional pillow).
After a few days, when the “scale of the disaster” becomes clear:
- The main advice that surgeons usually give to their patients during this period is to be patient and wait until the hematomas resolve naturally. There are no cases of them remaining forever, so you shouldn’t worry too much. In addition, there are no ways to significantly speed up their resorption.
- If a “clean” face is needed as soon as possible and time is running out, you can smear problem areas with products containing heparin - such as Badyaga, Hepatothrombin, Troxevasin, Traumeel S, etc. Their use must first be agreed upon with your surgeon.
- Massage of the problem area and physiotherapy can provide a slight improvement, but, as in the case of ointments, only a doctor should prescribe them.
↑ Advice from experts
| Salidzhanov Anvar Shukhratovich Doctor of Medical Sciences, leading plastic surgeon at the Mont Blanc Clinic: Rhinoplasty is a fairly severe injury to bone and soft tissue, so the appearance of hematomas after it is inevitable. As a rule, they completely disappear by the time the plaster cast is removed - i.e. in about 7-10 days. After this, the patient can already go to work, if it does not involve serious physical exertion. For women, to reduce the number of bruises, we select the date of surgery so that it does not fall on the period before or immediately after menstruation. During menstruation, the level of platelets is low, which means the blood does not clot well, and therefore severe hematomas almost always appear. Besides:
|
| Bely Igor Anatolievich plastic surgeon, doctor of medical sciences, professor, “DoctorPlastic”: Hematomas after rhinoplasty appear as a result of injuries to soft tissues and blood vessels. Their size depends on the volume of intervention, the characteristics of the blood coagulation system, and to some extent on the work of the anesthesiologist, but the main factor is the accuracy of the operation. They are usually located around the eyes. The duration of their resorption ranges from 7 to 14 days. The standard is about 10 days, but it’s better to count on 2 weeks. The use of ointments such as Traumeel, Sinyakoff and others containing heparin, as well as a number of physiotherapeutic procedures prescribed by doctors, will reduce the rehabilitation period. If on the first day after surgery the bruises continue to grow, a hematoma appears on the sclera (the white membrane of the eye), lacrimation begins, and pain appears, you should contact your doctor. This effect can develop within a week after removing the turunda from the nasal passages if nosebleeds occur, but such complications are extremely rare. |
| Kudinova Ekaterina Sergeevna plastic and maxillofacial surgeon, candidate of medical sciences: Bruises usually appear on the 2nd day after nose surgery, in the infraorbital areas and in the upper eyelids, sometimes also on the sclera of the eye (“red eye”). Their severity depends on the volume and type of operation; in most cases they will be clearly visible, since the skin here is very thin and almost devoid of fatty tissue. Normally, such hematomas disappear within 10-14 days. For some, they may linger longer - it depends on the individual characteristics of the body. But for those who worry too much, I can say for sure that there is not a single patient who would have them forever. To speed up resorption, physiotherapy is usually prescribed. But, in my opinion, they are effective primarily for combating swelling, but have minimal effect on bruises. It’s like with a runny nose: if you don’t treat it for a week, treat it for seven days. |
| Aleksanyan Tigran Albertovich founder and leading plastic surgeon of the Art Plastic clinic, Ph.D.: When performing rhinoplasty, incisions and detachment of soft tissues are made, which inevitably, to one degree or another, violates the integrity of the subcutaneous muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS), circulatory and lymphatic systems of the nose. Therefore, bruises usually appear after surgery. How voluminous they will be and how long the resorption will take depends on the specifics of the intervention, its complexity and methodology. For example, my proprietary method of subperiosteal detachment makes rhinoplasty virtually bloodless, which means the patient will have a minimum of hematomas, and they will go away very quickly. To speed up resorption, starting from 3-4 days, we carry out procedures of microcurrent lymphatic drainage, magnetic therapy and phototherapy, and also use special drugs: Troxevasin, ointments with arnica, Lyoton. It is useful for patients to know that with repeated surgeries and open rhinoplasty, bruising and swelling always last longer. This is due to a significant degree of disruption of the blood supply and lymphatic system of the nose during surgery. Therefore, I completely abandoned open rhinoplasty and do all, even the most complex, noses only using the closed method with a minimum of swelling and bruising. |
Measures to reduce the risk of hematoma formation after surgery
So, to avoid a hematoma after surgery, what should you do? For this purpose the following is carried out:
- Examination of the patient for the presence of blood-related diseases, in particular those related to blood clotting.
- Elimination of drugs that cause a decrease in blood clotting.
- Operations must be carried out with the obligatory restoration of blood loss.
- Damaged vessels must be carefully coagulated.
- After completion of the intervention, before suturing the wounds, it is necessary to check the cavity of the coagulated vessels.
- During the recovery stage, it is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s requirements, and this must also be done at the postoperative stage.
Do not forget that a hematoma is not so harmless and can negate the result of surgical actions. It is necessary to listen to doctors to avoid complications that may prolong the recovery period.
Prevention
Before surgery, each patient will undergo preparation - a series of measures aimed at reducing the number of complications during the rehabilitation period. In addition to other procedures, to reduce the risk of hematoma formation after surgery, consider the following recommendations:
- the patient undergoes a thorough examination to exclude the presence of diseases associated with decreased blood clotting;
- During the operation, it is prohibited to take medications that reduce blood clotting;
- During the operation, blood loss is immediately replaced;
- blood vessels damaged during surgery must be reliably coagulated;
- after the end of the operation, before suturing the wound, the surgeon must make sure that there is no bleeding in the cavity, and all vessels are well sealed;
- After surgery, the patient should follow the doctor’s recommendations before discharge and at home.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out by a traumatologist. In the absence of signs of damage to bones and joints, additional studies are usually not required; the diagnosis is made taking into account the medical history (the presence of a recent injury with a characteristic mechanism), the patient’s complaints and the results of a physical examination. For deeply located hematomas, ultrasound of soft tissues may be prescribed to assess the severity of the damage and differentiation from a bruise. If there is concomitant damage to hard structures, radiography of the corresponding segment is performed. In addition to bruises, differential diagnosis sometimes has to be carried out with fractures, tears of ligaments and muscles, less often with positional compression syndrome, acute myositis, ischemia due to thrombosis of a small or medium-sized vessel and some other conditions accompanied by dense local edema.
How to avoid negative consequences
- The choice of clinic and specialist should be conscious. To do this, you need to get acquainted with the opinions of other patients about the work of doctors, study certificates for equipment and other materials that will be used during implantation.
- At the preparation stage, you should not refuse additional examinations to identify all problematic issues that may become contraindications to the procedure.
- It is necessary to provide accurate information about your state of health, medication use, existing diseases (without hiding their exacerbation).