In this article we will talk in detail about what xeroderma is. Let's talk about the symptoms and types of this disease. You will learn why xeroderma appears in humans, and you will be able to see the consequences of the disease in the photo. You will also learn how this common skin condition is diagnosed and treated. After reading the information below and watching a video from a specialist, you will be able to independently recognize the disease and get rid of its symptoms in a timely manner.
What is xeroderma?
Xeroderma (xerosis) is a term used in medical practice when diagnosing patients with abnormal dry skin. The name comes from the Greek words "xero", which means "dry", and "derma" - skin. The disease is a type of pathology - ichthyosis. It occurs in a mild form.
Patients with this type of disease have excessively dry and rough skin, with very visible scales. Typically, xerosis affects the skin of the hands, face - in the chin area, the outer parts of the elbows and knees, feet, and the buttock area.
Xeroderma can be a problem for both women and men, but as medical observations show, most often it affects the female gender.
The risk group includes:
- Elderly people 60 - 75 years old.
- Pregnant women.
- Patients with diabetes mellitus.
- People living in countries with cold and dry climates.
- People working in conditions of constant humidity.
The appearance of xerosis is facilitated by disruption of the sebaceous glands, which reduces the production of subcutaneous fat. Its deficiency causes the skin to lose moisture, peel and wrinkle.
At a very advanced stage of the disease, painful cracks form on the skin. In addition, people with xeroderma should not be in direct sunlight. Dehydrated skin quickly burns in the sun and ages.
What is it and what do the signs of the disease look like?
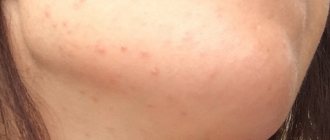
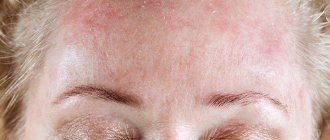
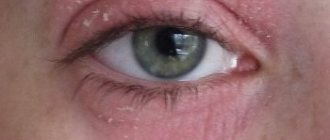
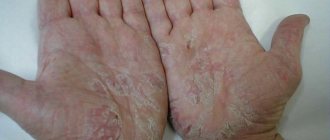
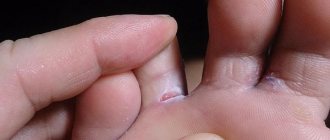
xerosis of the skin in the photo
Xerosis of the skin is a critical drying out of the epithelial layer with the destruction of a large number of its cells. Some scientific dermatologists who deal with the problem of the occurrence of this disease believe that xeroderma refers to the initial stage of skin ichthyosis. Xerosis is also present when the patient has certain types of infectious diseases.
Dry skin occurs when the sebaceous glands stop producing sebum or do so in reduced tone. The first symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- abnormally dry skin that does not show any external signs of hydration;
- as the condition of the skin deteriorates, its surface layer begins to form scales that peel off greatly;
- the affected areas of the epithelium become rough to the touch and it seems that the skin has become one continuous calloused neoplasm;
- mild itching, which gradually becomes simply unbearable, is present day and night, significantly reducing the patient’s quality of life;
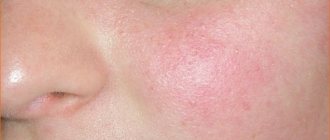
- swelling of the epidermal tissues, inflammation and redness, on which xeroderma develops;
- loss of elasticity of diseased skin, as well as the disappearance of pores that cannot be seen during visual inspection;
- very strong drying out of individual parts of the body with the formation of cracks from which lymphatic fluid is released.
In addition to the skin, xerosis can spread to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, nasal canals and organs of vision. People at risk are between 45 and 80 years old. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that its first signs are often confused with an allergic reaction to external environmental factors or banal dehydration of the surface epithelial layer.
Stages of disease development
There are 4 stages of development of xeroderma:
- It is practically asymptomatic. The person does not notice any structural changes in the skin (there is no wrinkling or itching), slight dryness is felt only on the feet.
- Over time, the skin begins to peel , thickens, becomes rough and hard. The patient constantly feels tightness of the skin. Begins to notice that from time to time itching and redness appear in certain areas of the body.
- Excessive exfoliation is observed. Painful cracks appear on the skin. Inflammation, itching and redness occur. In deep wounds, pus forms.
- This stage is characterized by a strong change in the structure of the affected skin. Trophic ulcers form (heal for a long time). The disease affects not only the protective layer of the skin, but also the dermis, which contains elements (elastin, collagen) responsible for the firmness and elasticity of the skin.
For reference: Symptoms of the first and second stages of xeroderma can be removed with the help of a deeply moisturizing cream, for example, such as “Losterin”. The third and fourth stages of pathology development require specialized treatment, including the use of medicinal antimicrobial and restorative drugs (see list below).
Xerosis. Symptoms
Manifestations of skin xerosis are specific:
- Skin tightness;
- Increased sensitivity;
- Frequent irritation and rashes;
- Redness;
- Invisible pores;
- Coarsening of the skin surface;
- Peeling and cracks (especially in fold areas).
People with xerosis suffer from itching and constant skin tightness. Sometimes there is a burning sensation. The symptoms worsen after contact of the epidermis with water and dry air.
In general, this disease includes four stages of development. Based on their description, you can also determine the presence of xerosis and its development:
- Stage one. The main criterion is functional impairment. The skin loses its protective properties. There is dryness and tightness, which do not cause much discomfort. For now, the problem can be solved with moisturizing creams and that’s enough. Tightness is often felt during facial movements. No wrinkles appear. Sometimes peeling appears after contact with water, sun or dry air.
- Stage two. The appearance and development of hyperkeratosis. Dryness and tightness are always present. Even after the cream. Cause significant discomfort. Small wrinkles begin to appear. Peeling becomes noticeable. Skin sensitivity increases and makes itself felt even with minor influences: contact with warm water, being in a room with an air conditioner running. From time to time, itching and redness bother you. The upper skin layer (epidermis) becomes thinner, its integrity is compromised, and hyperkeratosis (unhealthy epidermal thickening) appears.
- Stage three. Dermal hypotrophy. The peeling is large. Wrinkles are more obvious. Especially on the face (expression wrinkles). The deformation has reached the dermal layer (deeper than the epidermis). Any creams do not work. The skin is inelastic and looks stretched. Hard and rough to the touch. It's cracking. Sensitivity increases several times, inflammation appears.
- Fourth stage. Atrophy of the epidermal and dermal layers. Trophic type ulcers may form on the skin. Signs of premature aging appear.
Read also Genital warts (condylomas) - causes, treatment
Classification
Taking into account the reasons contributing to the occurrence of xeroderma, this form of pathology is divided into 3 types. So, xeroderma happens:
- Acquired - appears as a result of exposure to external adverse factors on the skin. A striking example is long-term treatment with external or systemic glucocorticoids (Betamethasone, Prednisolone).
- Senile is the result of the natural aging process. The skin is characterized by increased dryness, wrinkles and pigmentation.
- Constitutional (atopic) - its development is associated with hereditary predisposition, i.e. If in the family one of the relatives previously suffered from dry skin, then this form of pathology was inherited.
Note! Most often, symptoms of xeroderma can be seen on the skin of the hands, which are daily exposed to adverse factors, in particular contact with household chemicals.
A practicing dermatovenerologist will tell you more about the symptoms and forms of xeroderma, which is also called ordinary or vulgar ichthyosis, in the following video:
Causes of skin xerosis
Xerosis can have two main etiologies - congenital (atopic xerosis) or acquired.
If we talk about xerosis, which manifests itself in infants during the first months of life, then it can be a symptom of a mild form of ichthyosis. If we talk about acquired xerosis of the skin, then various unfavorable factors (reasons) can contribute to this.
Read also: How to get rid of warts?
Of course, by the cause of xerosis it is fair to designate the cause of hypofunction of the sebaceous glands, which leads to insufficient production of sebum by them, which is manifested by dry skin. Let's look at them.
Causes of xerosis (dry skin):
- Features of the skin – thin skin;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body (hypovitaminosis), especially vitamin A;
- exposure of the skin to direct sunlight (ultraviolet radiation), incl. visiting a solarium, as well as cold, wind, rain, snow, frost;
- frequent bathing in hot water, daily hot showers;
- use of soap with surfactants (surfactants) for washing the body;
- use of household cleaners and detergents without protective equipment (gloves);
- use of alcohol-based cosmetics;
- hormonal changes in the body, age-related changes;
- long-term use of hormonal agents - systemic and external glucocorticoid drugs;
- metabolic disorders;
- violations of the daily routine - work/rest/sleep;
- diseases of the endocrine system, skin, gastrointestinal tract: psoriasis, eczema, ichthyosis, dermatitis, keratosis pilaris, diabetes, gastroduodenitis, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, hypothyroidism, cancer.
Causes and provoking factors
External and internal factors can contribute to the occurrence of xeroderma. The first include:
- Poor or insufficient skin care.
- Wearing synthetic clothing (contributes to clogging of pores and causes irritation).
- Regular use of inappropriate cosmetic products.
- Taking a long course of hormone treatment.
Internal factors causing xeroderma:
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the body - the production of subcutaneous fat by the sebaceous glands is reduced.
- Hormonal imbalance - affects the functioning of the nervous system and vital organs (heart, liver, kidneys, lungs).
- Fungal infection - fungal diseases (mycoses: candidiasis, dermatomycosis, pityriasis versicolor) affect the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
- Kidney failure - causes dry and itchy skin, changes its color.
- Oncological pathologies of the skin - develop in the epidermal layer, disrupt metabolic processes, which causes degeneration of the skin.
- Diabetes mellitus causes skin diseases in 79.2% of patients.
- Hepatitis (liver disease) - disrupts the functioning of the sebaceous glands, contributing to the appearance of age spots and foci of inflammation.
Note! If the cause of xeroderma is internal factors, then its treatment is recommended to begin with their elimination. External triggers can be prevented, which will eliminate the occurrence of xeroderma.
Warning Tips
The problem of dry skin increases with age, and in order to slow down the appearance of external signs of old age (dryness, wrinkles, age spots), it is recommended to listen to the following tips:
- Avoid taking too hot a shower or bath.
- Do not spend a lot of time on hydromassage treatments or swimming in the pool.
- Use only gentle detergents; they do not contain dyes, fragrances or alcohol.
- After swimming, dry yourself with a soft towel without rubbing your skin, then apply moisturizer.
- Limit the use of soap on areas of skin affected by xerosis. But even on healthy-looking skin, use a mild soap containing moisturizing oils.
- At any time of the year, do not forget to use moisturizing lotions, especially in winter, when clothes do not allow the skin to breathe normally.
- In the summer, before going outside, apply sunscreen.
- Use a humidifier in your apartment, especially in winter, when heating devices make the indoor microclimate too dry.
This article provides detailed recommendations on how to care for and what to apply to dry skin to restore moisture balance.
General symptoms
Dry skin has specific symptoms and can be recognized without even touching the body. Typically, the skin looks irritated and tight. It shows inflamed, slightly reddish areas. Pores are practically invisible behind the exfoliating layer.
Below is a list of signs that accompany the occurrence of xeroderma:
- The skin quickly loses moisture; conventional moisturizing creams do not help normalize its balance. It becomes rough and wrinkled.
- After water procedures, a feeling of tightness appears, which disappears only after thoroughly moisturizing it.
- If left untreated, the skin begins to itch and peel.
- In place of the fallen scales, redness forms, then thin cracks, which become deeper over time, begin to bleed and hurt.
You need to get rid of the above symptoms immediately. At the first and second stages of development, people with xeroderma can be treated at home, following the recommendations of the attending physician.
In case of severe and large-scale skin damage, patients are advised to hospitalize, which, as a rule, begins with diagnosing the patient’s current condition.
When and which doctor should I contact?
A dermatologist treats skin diseases. And if you put off visiting a specialist, trying to cope with dry skin on your own, then you need to immediately contact him for help if:
- The affected skin began to ooze.
- Exfoliation of large areas of skin occurs.
- Annular erythema (ring-shaped spots) appeared on the body.
- The skin condition does not improve for a long time (even after treatment).
Note! Scratching dry skin can cause infection. As a result, you may develop a fungal or bacterial infection against the background of xeroderma, which will require specific therapy (see below for treatment methods).
Diagnostics
Before prescribing treatment for xeroderma, a dermatologist must differentiate the disease. In other words, clarify that this is xeroderma. After all, some skin pathologies, for example, eczema, have symptoms similar to it. This means that if you are diagnosed with eczema, the treatment plan will be different from the plan that is formed for a person with xerosis.
So, in order to diagnose xeroderma, you may be prescribed:
- Visual examination will help identify and compare symptoms.
- A skin biopsy will detect a fungal infection.
- Donating blood for biochemical analysis is necessary to assess the functioning of internal organs and identify deficiencies of microelements (potassium, magnesium, calcium, etc.) in order to replenish them.
To get a complete picture of your skin problem, the doctor will take a medical history (ask questions about current and previous diseases, ask whether there have been surgical interventions on the body, etc.).
Based on the data obtained, he will draw up a suitable treatment regimen using medications.
General treatment regimen
In order to rid you of xeroderma, the dermatologist will have to draw up a large-scale action plan, for example, like this:
- Elimination of factors that caused skin disease.
- Skin care using nourishing and moisturizing products.
- Treatment of affected skin areas with local preparations (ointments).
- Dieting.
Getting rid of the root cause
Treatment of xeroderma begins with eliminating the disease that contributed to the development of skin pathology.
For example, if xerosis was caused by a disruption in the functioning of the endocrine, nervous or immune system, then the primary task of the specialist is to eliminate it.
As a rule, after successful treatment of the described diseases, the functioning of the sebaceous glands returns to normal, and the condition of the skin improves.
If you do not pay attention to the disease in time, keratosis pilaris may develop.
Therapeutic care
To prevent infection (staphylococcus, streptococcus) from adding to dryness, which can happen through scratches and microcracks, it is very important to moisturize the skin.
Timely hydration and nutrition will allow the skin to gain elasticity, prevent cracks, wrinkles and a feeling of tightness.
Attention! For xeroderma, do not use cheap and universal creams (“Lumene Arctic Aqua 24”, “Nivea Creme”), they, on the contrary, help draw out remaining moisture. Make sure that the product you choose contains vitamins and vegetable oils, as well as animal fats.
For hygienic purposes, it is recommended to use products that do not contain surfactants; they reduce the level of sebum secretion, damage the outer layer of the epidermis and increase skin dryness. For this purpose, you can use gels (“Yves Rocher”, “Luxury of Oils”), which contain nourishing oils (argan, avocado), including essential oils.
Medicines for dryness and itching
Local treatment of xeroderma involves taking antihistamines (Suprastin, Diprazine), which help relieve itching that accompanies peeling of the skin. For severe xerodemic itching, you can apply a bandage using 1% Hydrocortisone ointment.
Ointments based on birch tar (Vishnevsky ointment) or naphthalene (Psori-Naft) can prevent the penetration of infections, which usually occurs through microcracks in the skin.
But if pathogenic microbes have already managed to penetrate the body, and purulent crusts appear on the skin, then the affected areas must be treated with antimicrobial agents.
Make lotions using the following preparations:
- 0.5% solution of silver nitrate - destroys bacteria, relieves inflammation.
- “Brilliant-Grun” (green) - copes with diphtheria bacillus and Staphylococcus aureus, is active against almost all pathogenic fungi.
- "Rivanol" - contains furatsilin, which kills staphylococci.
- 1% "Resorcinol" - for cauterization and disinfection of wounds.
Note! If xeroderma has entered the purulent stage, then you should not self-medicate. You should immediately contact a dermatologist, who, given the seriousness of the problem, may prescribe combined antibiotics (Triderm, Celestoderm-B) or corticosteroid drugs (Advantan, Elokom).
Keratolytic therapy will help remove dead scales from the skin, including treating the skin with products containing salicylic and lactic acid (Aven Akerat, Uriage Keratosan, La Roche Posay) or urea.
Such creams help unblock sebaceous plugs, have a softening effect on the skin and help normalize its breathing.
Nutrition tips
- Eat more vegetables, raw and cooked.
- The menu should always include porridge (buckwheat, oatmeal, rice). The microelements they contain not only improve the condition of the skin, but also strengthen the immune system.
- Use steamed fish and meat dishes, this way you can retain more nutrients in the food.
- Drink 1.5-2 liters of liquid per day (water, herbal tea, dried fruit compote) so you can protect your skin from dehydration.
- Eat fruits and berries, nuts every day.
- Eliminate smoked, fried, and spicy dishes from the menu.
- Do not eat fast food, chips, etc. products.
- Forget about drinking alcohol.
Treatment of skin xerosis (dry skin)
Treatment of dry skin (xeroderma) includes the following points of therapy:
1. Elimination of the root cause of dry skin; 2. Nourish and moisturize the skin; 3. Local treatment of dry skin areas; 4. Diet; 5. Compliance with preventive measures to prevent dry skin.
Addressing the root cause of dry skin
Treatment of skin xerosis is carried out based on the diagnosis of a dermatologist, who must determine the cause of this pathology.
If the cause of xeroderma lies in diseases of the endocrine, nervous, immune, gastrointestinal tract and other systems, then therapy is aimed at their treatment, and with the right actions, after getting rid of those diseases, the functioning of the sebaceous glands will be restored automatically.
Nourishes and moisturizes the skin. Skin care
Due to the fact that dry skin means there is no protective layer on it, the skin needs to be moisturized and nourished. This must be done to prevent pathogenic microflora, for example, staphylococcus, streptococcus and other bacteria, from entering the body, or the skin layer itself, through micro-traumas of the epidermis. If this is not done, then a secondary infection with its own complications may join the dryness.
Moisturizing and nourishing the skin also gives the skin elasticity, which helps prevent the appearance of cracks, stretch marks, and wrinkles on the skin. Moisturizing also relieves itchy skin.
However, remember that you cannot moisturize your skin with many cheap moisturizers, because... they draw out the remaining moisture from already dry skin. It is best to moisturize the skin with products containing substances such as: vegetable oils (olive, flaxseed, almond), animal fat (bear, greyhound), vitamins, etc.
The best way to moisturize your skin is to drink plenty of liquid – up to 3-4 liters per day. Shouldn't lemonade be the dominant drink?
For your washing, use products without surfactants (surfactants), which disrupt normal sebum secretion, remove the protective film from the skin, thereby increasing dryness of the skin.
Shower gels with a skin moisturizing effect, which contain various oils, incl. ethereal. There is also soap with a moisturizing effect. Yes, these products are usually more expensive, but your health is worth it.
An air humidifier also has a beneficial effect on the skin, especially in winter, when the air in residential areas becomes dry due to heating.
Local treatment of xeroderma
To relieve skin itching, you can take an antihistamine: Suprastin, Claritin, Diprazine.
To relieve itching locally, you can apply a bandage soaked in novocaine to the itchy skin.
For severe itching, you can apply a bandage of weak hormonal ointment - 1% hydrocortisone.
In case of microcracks, in order to prevent infection from entering the body, it is advisable to disinfect the skin by treating it with ointments and creams based on tar and naphthalan.
In case of microbial damage to the skin: if various crusts of a greenish-yellow hue begin to form on the skin, these areas can be treated with antimicrobial lotions: 0.25-0.5% silver nitrate, Brilliantgrun, Rivanol, 0.5 -1% “Resorcinol”, copper sulfate solution. But at the first such symptoms, immediately see a dermatologist!
Read also Red papilloma - treatment, removal
To remove the top layer of scaly epidermis, keratolytic therapy is performed, which is based on treating the skin with creams and ointments with components such as salicylic or lactic acid, urea. These creams soften the skin, remove sebaceous plugs and dead scales, and help normalize the breathing of the epidermis.
Diet for xeroderma
Diet is an integral part of the treatment of many diseases. This is due to the quality of modern food. The fact is that from year to year, less and less healthy food is sold on store shelves. More and more food products are inventions of the chemical industry, artificial products from greenhouses, etc. This food does not contain the necessary vitamins and substances that, when sufficiently supplied to the body, contribute to normal growth, development and human health. Thus, often, diet alone is able to concentrate the body on any failures that have occurred in it, and solve them on its own.
A diet for xeroderma implies the exclusion from the diet of fatty, fried, spicy and smoked foods, fast food, alcoholic beverages, various store-bought chips, crackers, etc.
What can you eat with xeroderma: firstly, drink more fluid, up to 3-4 l/day, secondly, eat foods rich in vitamins and microelements - raw vegetables, fruits, berries, nuts, cereals, fish.
It is worth noting that the least loss of vitamins and other useful substances in food occurs when steaming, so a steamer is an integral household appliance recommended by many nutritionists.
For dry skin, special emphasis should be placed on additional oral intake of vitamins A (retinol) and E (tocopherol). B vitamins are also indicated because most of them, if not all, directly affect the normalization of the cardiovascular system. It’s no secret that low-health food leaves in the human body, especially in blood vessels, remnants of “bad cholesterol”, which over the years disrupts normal blood circulation in many organs, clogging blood vessels, especially disturbances appear in blood vessels with a small lumen (veins, capillaries) . B vitamins help cleanse and quickly remove “bad” cholesterol from blood vessels, blood nourishes all human organs and systems, normal metabolism occurs, and the body begins to function with maximum efficiency.
Additional treatment for dry skin
Beneficial to the surface of the skin, i.e. When treating dry skin (xeroderma), the following procedures are used:
- ozone therapy;
- mesotherapy;
- skin treatment with microcurrents (darsonvalization).
Folk remedies
Below are several recipes that will help you cope with the initial stages of xeroderma.
In addition, we recommend using these recipes during the cold off-season, when skin health especially needs support.
Bath "Cleopatra"
Ingredients:
- Fresh warm milk - 4 tbsp.
- Natural liquid honey - 0.5 tbsp.
- Warm olive oil - 5 tbsp.
How to prepare: Mix all ingredients. Pour the mixture into a bathtub with water at a comfortable temperature.
How to use: Lie in the healing liquid for 15-20 minutes. Dry your body with a soft towel without rubbing. Apply a cream with a restorative and moisturizing effect, for example, La Roche Posay, which is often recommended by dermatologists.
Result: You will be able to notice an improvement in skin condition after the first procedure. When you take such a bath every day, you will forget about the problem with xeroderma forever.
Hot compress for face
Ingredients:
- Mint petals.
- Calendula flowers.
- Linden blossom.
How to prepare: Take equal parts of the ingredients, pour boiling water over them, cover the container and wrap it up. Let the mixture sit for 10 - 15 minutes.
How to use: Soak a soft towel in the herbal infusion, cooled to a comfortable temperature. Apply to your face for 1.5 - 2 minutes. Repeat the procedure 5 - 6 times. Lubricate your skin with a nourishing cream; the Riche Desalterante cosmetic product has proven itself well in this regard. (Clean 2 times a week).
Result: The compress expands and cleanses pores, removes peeling.
Question answer
What to do if in winter the symptoms of xeroderma worsen and the body is very itchy? (Previously, Aevit vitamins and Belobaza moisturizer were prescribed, but they did not help).
Change your moisturizer to a stronger one, such as Locobase or Lipikar Up. Drink more fluids, normalize the humidity in the room.
Is it possible to get xeroderma?
The disease is not contagious, since the cause of the formation of scales on the skin is a disruption of the sebaceous glands.
The child was one year old when he was diagnosed with xeroderma, which later caused dermatitis. Sores appeared on the skin, and the itching made the child restless, especially at night. What should care be like?
Discuss with your dermatologist the prescription of the antiallergic drug Fenistil in drops, as well as hormonal ointments. Eliminate soap completely from your baby’s hygiene routine. Use fatty creams to moisturize the skin (2-3 times a day). Locobase Repea and Topicrem are suitable.
Is it possible for xerosis to transform into a malignant form? Is it possible to excise dark formations on the skin?
The likelihood of malignancy of xeroderma foci is not high. Scab removal can be performed for aesthetic purposes using cryodestruction (liquid nitrogen).
Is it possible to get rid of xerosis only with folk remedies?
This is possible if the disease is at an early stage of development.
What to remember:
- Xeroderma is a mild type of ichthyosis; it is characterized by constantly dry skin.
- The disease is not contagious and appears in individuals with reduced sebum production from the skin.
- Abnormal dryness of the skin can be caused not only by xerosis, but also by other diseases, such as eczema. Therefore, skin treatment cannot begin until an accurate diagnosis is made.
- Proper nutrition plays an important role in the treatment of xeroderma.
- The most important thing is to drink plenty of fluids.
Treatment
If a patient has symptoms of skin xerosis, a dermatologist conducts an initial examination of the epithelial layer affected by the disease, and then prescribes a comprehensive examination of the body. The primary goal in the treatment of xerosis is to determine the presence of a cause that provoked critical dry skin. In most cases, these are not only external environmental factors, but also diseases of internal organs. After this, the patient may be prescribed treatment for skin xerosis, which consists of the following:
- Consumption of synthetic vitamins and minerals containing high concentrations of vitamin A and E.
- Drink plenty of fluids with daily consumption of clean water according to the schedule drawn up by the attending dermatologist. Most often, it involves drinking 1 glass of drinking water every hour.
- Applying moisturizing creams and masks to the sick skin, which are selected exclusively by the doctor involved in the patient’s therapy.
- Treatment of skin areas that show signs of xerosis with hormonal ointments such as corticosteroids. Their use is justified when a person has stage 3 of xeroderma development, which threatens to develop into the formation of trophic ulcers.
- Hydrocortisone. A medicinal product for external treatment of the epithelial layer affected by xerosis. The ointment relieves itching, swelling, eliminates the inflammatory process and promotes the healing of cracks, if any.
The duration of treatment for xeroderma of the skin depends on the severity of the disease, as well as the individual qualities of the patient’s body. If the cause of the dermatological disease was discovered in a timely manner, the duration of therapy is about 1 calendar month. Recovery is possible in a shorter time, but not earlier than 3 weeks.