Benign neoplasms on the skin
Also, constant exposure to the sun increases the risk of skin cancer. Poor exposure to sunlight on the skin is the main cause of the disease. In general, people who spend a lot of time in the sun are more likely to develop skin cancer. A sunburn that occurs once, mainly in children, increases the percentage of melanoma development many times over.
Skin cancer symptoms vary greatly. In some patients, minor shiny skin diseases are detected. For others, the growths are red and hard to the touch and may sometimes bleed. If such symptoms appear, a doctor's examination is necessary.
Neoplasms can also recur; they are metastases of malignant tumors. They may also be the first symptoms of cancer, helping to diagnose it. Metastases indicate the location of the tumor, as they occur quite close to it. In most cases, metastases result from lung cancer, colon cancer, oral cancer, kidney or stomach cancer, and breast cancer.
The most common benign neoplasms include fibromas, papillomas, lymphangiomas, lipomas and leiomylomas.
Papillomas are small in size and have a thin or wide stalk. They have an uneven surface, white or brown. They are placed on the skin either individually or in clusters.
Fibroids occur on any part of the body and can be hard or soft. Solid fibroids are made of fibers and have a small number of cells. They occur mainly in the vagina or chest walls. The mild form of fibroma forms in the subcutaneous tissue and is found on the genitals. Such formations are most often removed surgically.
Lymphangiomas are found mainly at birth and are divided into cystic, cavernous and capillary. They may take on a bluish color. Lymphangiomas occur on the upper body, head or arms.
Lipoma consists of adipose tissue. It develops slowly and sometimes reaches large sizes. It is soft to the touch and has a capsule. It can also be removed through surgery.
Leiomyoma arises from muscle tissue mainly as a result of trauma. Formed in the tissues of the scrotum or labia.
Angiofibromatosis of the skin occurs in young adults or children. It occurs in the abdominal or chest wall, develops slowly or, conversely, quite quickly.
Neurogenic tumors occur in different parts of the body and are particularly painful.
Wen are benign changes in subcutaneous adipose tissue, which quite rarely turn into malignant formations. The seal appears to be round in shape. Most often they are removed for aesthetic reasons.
How is melanoma different from cancer and moles?
Melanoma is not a cancer, but a malignant process that develops from pigment-containing cells - melanocytes. The overwhelming number of melanocytes are located in the skin, but can also be in other tissues, in the eyes, internal organs and mammary glands, and the gastrointestinal tract. Melanoma of the skin and, for example, melanoma of the eye are not very similar in course and treatment; they are united by a common “place of birth” - the melanocyte.
Melanoma and nevus are also related by a common parent cell, but there is no reliable evidence that melanoma can develop from a nevus. Congenital nevus is very rare; it is an “acquired” skin lesion. Moles actively appear in youth, and then as the skin ages, they become more and more numerous.
Carriers of large nevi with an unusual color or with frequently appearing moles benefit from regular observation; modern computer diagnostics using FotoFinder equipment allows you to clinically evaluate “old” moles, notice new spots in time and identify unfavorable symptoms.
Precancerous skin growths
Scientists have still not proven which tumors are precancerous and which are the initial stage of cancer itself. Let's consider xeroderma pigmentosum, actinic keratosis, keratoacanthoma, cutaneous horn.
The tumor called xeroderma pigmentosum is of genetic origin. This disease occurs in childhood. A person with this disease should avoid exposure to sunlight, as even short-term exposure to the sun causes red spots that create areas of pigmentation and look like freckles. Over time, such spots form areas of thin and dry skin.
Actinic keratosis, also known as solar keratosis, occurs on exposed areas of the skin. It is characterized by yellowish rashes with a diameter of no more than one centimeter. Then such rashes become covered with scales or dry crusts, which begin to bleed when torn off. If such a formation begins to bleed on its own, this is the beginning of the stage of a malignant tumor.
Paget's disease occurs in women closer to fifty. It is localized either around the nipple or on the nipple itself. A crust appears in this area and the nipple begins to retract. This condition can take about ten years to develop, and is generally the initial stage of cancer.
Definition of neoplasms and their types
New growths on the skin arise due to uncontrolled division of epidermal cells. Most of the growths do not bother a person throughout life and do not cause complications. On the skin they are represented by primary and secondary tumors, nevi, hemangiomas.
The exact causes of growths have not yet been established, but doctors have identified factors that can serve as an impetus for disruption of the mechanism of cell division of the skin. Among the most common are the following:
- Abuse of bad habits. Smoking, frequent consumption of alcohol and other prohibited substances have a detrimental effect on the entire human body. Toxins introduced into healthy tissue through tobacco smoke and alcohol can affect the ability of cells to divide and function normally. As a result, pathological growths form on the skin.
- Genetic predisposition. If blood relatives have had cases of multiple tumors appearing on the body, the child will also always be at risk.
- Reduced protective functions of the body . Weak immunity is not able to fully control and destroy pathological cells, as a result of which they begin to divide uncontrollably.
- Ultraviolet rays and radiation. Overdose of UV rays or excessive doses of radiation disrupt the normal functioning of healthy cells, causing them to divide and grow much faster.
- Chronic stress. Nervous overload and stress negatively affect the entire body, reduce immunity, and cause the development of many dangerous diseases, including skin ones.
- Poor nutrition. A person who eats junk food, poor in nutritional components, vitamins and elements, is more prone to various diseases than others. A skin tumor occurs as a result of immune dysfunction that occurs against the background of a deficiency of vital substances.
Depending on the etiology, the following types of skin tumors are distinguished:
- Benign . The cells of these growths partially retain their normal functions. They are characterized by stable sizes and the absence of metastases. The structure of such formations is similar to healthy tissue, so they do not threaten human life and health. If the tumor does not increase, does not cause discomfort and does not interfere with the person, there is no need for special treatment. If the growth, for example, is constantly injured or it becomes noticeable that its size is becoming large, you need to visit a dermatologist, who will most likely offer to remove it.
- Precancerous . They are a formation whose cells, under the influence of negative internal or external factors, have changed and can at any time degenerate into malignant ones.
- Malignant . A skin neoplasm of malignant etiology grows aggressively and rapidly, penetrates healthy tissue, and spreads metastatic cancer cells throughout the body. The prognosis of such a pathology depends on the stage of progression; in addition, malignant tumors tend to recur, so surgical removal does not guarantee a complete cure. If the formation has metastasized and spread to healthy tissue, the chances of recovery and recovery are minimal.
Growths on the scalp
A growth on the scalp is often benign in nature. It could be:
- mole;
- wart;
- hemangioma;
- seborrheic keratosis.
However, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor if a formation that has not previously bothered you manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- pain;
- bleeding;
- itching;
- peeling;
- suppuration.
Growths on the skin of the face
Neoplasms on the skin of the face are most often presented in the form of:
- papillomas;
- warts;
- milia;
- keratome
All these growths of benign etiology do not pose a threat to human life, but can cause aesthetic discomfort. Therefore, the cosmetologist will advise you to get rid of the problem.
Growths on the skin of the hands
The presence of growths on the skin of the hands also often causes aesthetic discomfort, especially in women. The following tumors most often appear in these areas of the body:
- cysts;
- neurofibromas;
- papillomas;
- warts
It is important to always monitor the condition of such growths and, if suspicious symptoms arise, do not hesitate to visit a doctor.
Growths on the skin of the legs
A common reason for the appearance of growths on the skin of the legs is wearing uncomfortable shoes, which leads to impaired blood circulation in the tissues of the lower extremities. Such formations constantly remind a person of themselves with acute pain, discomfort and even bleeding. If you do not get rid of the pathology in the early stages, the risk of dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system increases.
Precancerous skin tumors in old age
Precancerous tumors are very dangerous. Such formations include Keir's and Bowen's diseases, senile keratoma and cutaneous horn.
Cutaneous horn occurs in older people in places that are most susceptible to pressure or friction. The tumor has the appearance of a cone-like formation.
Senile keratoma also occurs in most cases in elderly people. It consists of layers of epithelium and is round in shape with dense crusts on top. It occurs mainly in open areas of the body and rarely develops into a malignant tumor.
Queyre's disease is characterized by painless red nodules on the genitals, but frequent trauma causes pain and bleeding. In rare cases, the tumor develops into a malignant tumor.
Bowen's disease develops within the epidermis and manifests itself as spots on the skin that combine to form large surfaces. Among the factors predisposing to such a disease will be the presence of warts, which are caused by the papilloma virus. Due to the polymorphism of the cells of such formations, this disease often ends in cancer.
How does basal cell carcinoma differ from squamous cell skin cancer?
Cancer arises only from an epithelial cell, to which the melanocyte is not related, although it lives nearby in the skin or mucous membrane. Basalioma and squamous cell carcinoma develop from cells of different layers of the skin epidermis, which becomes the basis for their differences.
For more than a century, it was believed that basal cell carcinoma was not entirely malignant, but rather a borderline process between good and evil. The basis for this was the belief that basal cell carcinoma does not metastasize, although the high ability to relapse and aggressiveness towards surrounding tissues were not in favor of benignity. By the beginning of the 21st century, sufficient literary material had accumulated on cases of metastasis of basal cell carcinomas; as a rule, these were either mixed basal cell carcinoma or a scleroderma-like form of basal cell carcinoma “morphea” that does not form skin ulcers.
In most cases, basal cell carcinoma grows not so much in breadth as in the tissues, preferring the scalp; it rarely metastasizes, often recurs after treatment, and is prone to the simultaneous formation of several foci of cancer at once. Of all skin cancers, basal cancers account for two-thirds.
Squamous cell carcinoma spreads widely and deeply, often metastasizes and recurs. He accounts for every fourth patient with a malignant skin tumor.
Malignant neoplasms
Neoplasms, or so-called skin disease, occur when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrolled. Most of these neoplasms are benign - these are moles and birthmarks. But still, skin cells tend to mutate into malignant ones. If such neoplasms are not detected in the early stages, they can spread to other organs. Skin cancer is the most common disease. There are many types of skin cancer. Malignant neoplasms are quite common and elderly people are most often susceptible to such diseases. Malignant formations differ from benign ones in that already at the initial stage the cells cannot perform their functions and can affect neighboring tissues and organs, spread through the lymph and blood vessels, and cause tumors throughout the body. Such neoplasms can safely include melanoma and sarcoma.
Melanoma ranks first among the most malignant tumors. Pigment spots on the skin, which can be either congenital or acquired, predispose to this disease. Older women with blond hair and blue eyes are found to be most susceptible to melanoma. Melanoma occurs on the upper and lower extremities, and damage, trauma to moles or exposure to chemicals can lead to the development of a malignant neoplasm. The most common symptoms that indicate the growth of a neoplasm into a malignant one include an increase in size, frequent bleeding and changes in pigmentation.
Sarcoma is quite common in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome, more often in male patients. Sarcoma appears on the lower extremities in the form of purple spots; such formations tend to unite. In patients with the immunodeficiency virus, the disease progresses quite quickly and affects the lymph nodes, which spread the disease throughout the body.
Epithelioma is the name given to skin formations from epithelial cells in the form of pink nodules on the skin of the external genitalia, which become covered with a yellowish crust over several years. As a result, the tumor begins to bleed and the disease spreads through the lymph nodes throughout the body. Death occurs due to bleeding, which is caused by damage to blood vessels and tumor disintegration. Treatment is performed surgically and, if necessary, chemotherapy is performed.
A tumor of the skin appendages is characterized by the occurrence of changes in the sebaceous glands or hair follicles and sweat glands. In most cases they are benign, but there are also malignant ones. They are removed surgically.
Types of skin formations
There are two types of benign formations: congenital and acquired. Warts and moles of various shapes and colors are considered congenital formations. Acquired pathologies are recognized as superficial and subcutaneous formations that arise as a result of metabolic dysfunction, decreased immunity and viral diseases.
The classification of congenital and acquired skin diseases is varied. Each type of skin growth exhibits its own shape, color, structural features and signs of occurrence.
Neurofibroma
The cell that forms the nerve sheaths becomes the foundation for the growth of neurofibroma. The formation looks like a tubercle, hard to the touch, reaching three centimeters in diameter.
Human neurofibromatosis
Neurofibroma can be single or multiple. Multiple formations are called neurofibromatosis and are considered the consequences of a genetic failure that is inherited. Single pathologies rarely transform into malignant tumors, but bring the owner significant discomfort and pain. The skin tubercle is characterized by abundant pigmentation - most often the tumor is brown, red or dark brown. Neurofibroma is located in the subcutaneous tissue of the epidermis.
The disease is characterized by the absence of symptoms at the initial stage of development. Reaching an impressive size, the tumor puts pressure on the nerve endings, and the patient experiences pain. Locations: on the face, on the skin of the back, abdominal cavity, arms, leg. The first symptoms of neurofibroma are brown or red spots in various areas of the human body. Neurofibroma can be cured with conservative therapy or surgery.
Fibroma
Connective tissue is the main component of fibroids. The tumor has a dense consistency, is hard to the touch and is characterized by a light pink tint. This neoplasia reaches a maximum of three centimeters and occurs mainly in women who have reached the age of twenty.
There are soft and hard types of fibroma. A hard skin growth forms near the upper layers of the skin. Soft fibroma is a movable and soft-to-the-touch pouch that appears on the neck, chest, armpits and groin folds in women who have reached adulthood. It is not uncommon for a black or gray fibroma to appear on the human body, showing a smooth surface. Doctors recommend removing fibromas: there remains a risk of metastasis and transformation of the pathology into fibrosarcoma, even under favorable conditions. Regular physical and chemical damage to the tumor provokes rapid growth and the occurrence of skin cancer.
Fibroids can be cured using traditional surgical removal with a scalpel, laser, electrocoagulation and radio wave method. Laser and radio wave methods exclude further recurrence of the pathology and give favorable prognoses.
Desmoid fibroma
Lipoma
A neoplasm formed from fatty tissue and localized in the layer of connective tissue is called lipoma or wen. Reaching a large size, the lipoma grows into nearby tissues and reaches the bone surface. Often the tumor spreads to neighboring muscles and blood vessels. The lipoma is round in shape and soft to the touch. The human body can be affected by both single and multiple wen. They appear in any part of the body where there is a fat layer, which is a favorable environment for the development of this skin disease. Locations can be different: wen affects the face, neck, back, upper and lower extremities, head, eyelids and mouth.
The occurrence of the disease does not depend on gender predisposition, body weight or heredity. Pathology appears in men and women, in children. Fatty tissues do not pose a particular danger to human life, but sometimes transformation into liposarcoma is noted. To avoid unwanted transformation, doctors recommend removing the tumor in the early stages of development. This tactic will also help to avoid cosmetic defects at the surgical site. Methods of treatment and removal of wen include surgery using a scalpel, laser method, radio wave and puncture-aspiration principles for eliminating pathology.
Atheroma
Blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands provokes the appearance of a residual cyst - atheroma. This tumor consists of products produced by the sebaceous glands, present in the form of a curd mass that has no odor. On palpation, a dense consistency and clear contours of the pathology are noted.
There are single and multiple atheromas. The phenomenon of multiple atheromas is called atheromatosis. Superficial atheromas predominantly occur, the localization of which can be different: on the back, head, neck, face, in the thigh, groin, lower and upper extremities of a person. The occurrence factors include non-compliance with hygiene rules, injuries to the hair follicles, metabolic diseases and unprofessional depilation.
Atheroma on the neck
With regular physical and chemical exposure, atheroma turns into an inflammatory and edematous state and acquires a red tint. If an infection gets inside the tumor cavity, pus accumulates and spontaneously erupts with a sebaceous consistency.
Dermatologists and oncologists advise removing atheroma that has reached a small size, since there is a risk of transforming the pathology into liposarcoma. The malignant version of atheroma is characterized by rapid growth, compression of surrounding vessels, nerve endings and nearby tissues. Liposarcoma poses a danger to human life, as it provokes anemia, vascular blockage, intoxication syndrome and metastasis to the internal organs of a person.
Lymphangioma
This type of tumor is congenital and occurs as a result of pathological changes in the lymphatic vessels. In rare cases, the pathology is acquired. A congenital neoplasm is formed as a result of dysfunction of the outflows of lymphatic vessels, which provokes changes in the structure of the vessel lining and the appearance of a tumor-like growth. The acquired form of the disease appears as a result of infectious lesions of the human skin.
The pathology looks like a blue growth rising above the skin. On palpation, a dense consistency and clear boundaries of the pathology are noted. Sizes vary from one to five millimeters. Children under three years of age are at risk of developing this condition. During the development process, there is a slow growth of the formation with spasmodic periods when the growth rapidly increases in size.
When lymphangioma occurs, only surgical intervention is used, since the growth often puts pressure on such vital organs as the larynx, lungs, and trachea. Modern methods of eliminating the tumor are sclerotic injections into the growth cavity, cauterization using diathermocoagulation, electrocoagulation and freezing the growth using cryodestruction.
Human lymphangioma
Wart and papilloma
Infectious infection of the skin and mucous membranes provokes the appearance of the papilloma virus, which manifests itself in the form of warts on various areas of the human body. The growth has distinctive features: multiple and single nodules of various shapes of brown, flesh-colored or light pink, reaching several centimeters in diameter.
Skin growths have different habitats: on the face, neck, groin area, genitals, on the back and abdominal cavity of a person. Localization of papillomas in the area of internal organs was recorded. Warts and papillomas appear as a result of nervous tension, frequent stress, autonomic disorders and decreased immunity. The skin disease is transmitted through sexual contact and through the general use of hygiene products such as washcloths, towels, and hair removal products.
Warts rarely metastasize into cancer and do not pose a threat to human health.
Getting rid of papilloma involves complex therapy, which includes strengthening the immune system, maintaining proper nutrition, introducing physical activity, taking medications and removing skin growths in case of pain or discomfort. Papilloma can be eliminated using laser coagulation, freezing using cryodestruction and electrocoagulation.
Nevus and mole
This neoplasm manifests itself in the form of excessive pigmentation on the skin. Shape, size and color are varied. A nevus can reach several tens of centimeters in diameter. The accumulation of nevus pigment cells can be congenital or acquired. There are also benign and malignant pigment spots. The first category is characterized by symmetrical, clear shapes, the same color shade and dimensions reaching five to six millimeters. Metastatic skin pathologies have uneven and asymmetrical edges, a multi-colored pigmented surface and dimensions of more than six millimeters.
Factors that provoke the occurrence of congenital pigmentation include the influence of toxic compounds and electromagnetic radiation on the fetus in the womb, diseases of the internal organs of the lower pelvis, genetic predisposition and the occurrence of pathologies during pregnancy. The appearance of acquired moles is influenced by hormonal imbalance in adolescence, mechanical damage to the skin, oral contraceptives, harmful ultraviolet radiation and infectious diseases of the skin. A large number of nevi are observed in men and women who have reached the age of twenty-five.
Hemangioma
The described type of skin tumor affects the walls of blood vessels and forms in the subcutaneous layer of the body. Hemangioma rises above the surface of the skin and is not subject to pigmentation. The pathology is characterized by rapid spontaneous growth and a decrease in volume when pressed. Mostly the pathology occurs in children during the first years of life. The places where hemangioma occurs can vary, but it mainly appears in the head and neck area. Cases of hemangioma of internal organs have been recorded. There are a number of types of skin pathologies:
- With cavernous hemangioma, there is a deep location of the pathology in the skin layers of the human body. The formation has the shape of a node and a blue tint. Diagnosed immediately after the birth of the child.
- With capillary hemangioma, the occurrence of pathological changes in the epithelial layer has been recorded, covering large areas of the skin and having a red or blue color.
- With combined pathology, the simultaneous appearance of cavernous and capillary hemangioma is observed.
- The mixed form of skin disease involves the process of involvement of the vascular membranes and connective tissues.
The disease appears as a result of hormonal characteristics of the fetus, infectious diseases of the pregnant woman in the early stages and taking medications during pregnancy.
Capillary hemangioma
Inflammatory processes of hemangioma cause complications such as open bleeding, which can only be restored through surgery. When localized near a vital organ and rapidly increasing in size, the tumor can interfere with the functioning of nearby organs and tissues and, thereby, worsen the patient’s quality of life. To remove this skin defect, a sclerosing method is used, which causes necrosis of the hemangioma, cryodisruption, coagulation and traditional surgery.
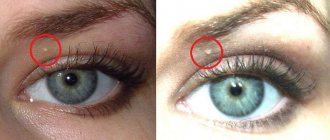
Keratoma
The basis of this skin tumor is keratinocytes, which form the stratum corneum of the skin. Dead cells transform into a growth, which is a spot or nodule covered with a crust. Keratoma has different locations and most often occurs on the back, head, face, lower and upper extremities. This type of skin pathology requires urgent treatment, since the keratinized cells that form the keratoma are similar to the cells of malignant tumors.
Single and multiple keratomas are distinguished. The second type of pathology occurs extremely rarely and there is a maximum of three skin nodes. The formation of multiple neoplasms in one area of the body indicates the risk of developing skin cancer. The causes of formation include pathological changes in cell functioning, hormonal imbalance, harmful ultraviolet radiation, genetic predisposition and vitamin deficiency. The following types of keratomas are defined:
- With solar neoplasm, the formation of flaky spots reaching several centimeters in diameter is observed. The growth does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient. Common places for tumor localization: hand, foot, face and torso.
- A horny neoplasm forms as a light brown or gray spot protruding above a person’s skin. The growth protrudes significantly above the surface of the skin and peels off profusely. Common sites of occurrence include the eyelids, forehead, lips, cheeks, nose and mucous membranes.
Skin keratoma near the eye
- With senile keratoma, dense light brown spots appear, reaching several centimeters in diameter. As the build-up develops, multiple layers are formed that gradually crack. This type of keratoma grows slowly and is localized mainly in the head, back, chest and in parts of the body rich in hair.
- Follicular formation is light pink and flesh-colored nodules, reaching two centimeters in diameter. The surface of the keratoma is covered with tubercles and rises above the skin of the body. Mostly this tumor appears on the lower extremities, lips, cheeks, nasolabial folds and palms.
If the tumor does not pose a risk of becoming a cancerous tumor and does not reach a large size, doctors recommend using medications and alternative methods of treatment. At the slightest suspicion that a skin growth has transformed into a cancerous tumor, experts recommend tumor removal. Keratoma can be eliminated using cryodestruction, radio wave method, laser, electrocoagulation and traditional surgery.
Dermatofibroma
This type of neoplasm occurs as a result of capillary changes and consists of connective tissue. The tumor is characterized by a lack of pain and slow development. The formation is a rounded, deep-lying node protruding several millimeters above the surface of the skin. Mostly the growth occurs in young women who have reached the age of thirty.
Poorly differentiated form of skin cancer
A low-grade form of cancer has characteristically arranged cancer cells. Their peculiarity is the difference between cells within the same tumor. They have irregularly shaped nuclei that are unevenly distributed. A poorly differentiated form of cancer causes enormous changes in cellular structure. This form of cancer is characterized by rapid cell division. In appearance, such cells resemble stem cells, which are maternal and go through several stages. This disease has a high percentage of malignancy. One of the most dangerous is low-grade breast cancer, which grows and infects other organs. It is characterized by penetration and metastasis into the axillary lymph nodes. Dividing cancer is difficult to diagnose, since the tumor density is low and differs little from other tissues.
Poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma also affects the skin. Symptoms of this disease: bleeding and rash, ulcers or erosions, crusts, soft red formations with a rough surface. They are mostly single, but are also found in multiple quantities. Such tumors form on the body or face, as well as on the genitals. This type of cancer typically metastasizes to nearby lymph nodes.
Such formations are small in size, but despite this, they are very dangerous. The pea-sized tumor shows few changes, but often grows into blood vessels and spreads cancer cells throughout the body. These forms of cancer are always fatal.
Diagnosis of skin tumors
Most often, a person who finds a tumor on his body seeks advice from a doctor. But regular dispensary examinations provide very good results for diagnosing diseases in the early stages. The doctor, having examined the tumor, can determine the pathological condition and prescribe further tests to the patient, and then treatment. Also, if skin changes form for no apparent reason, you should be examined by a dermatologist and oncodermatologist. With the help of research, the positive or negative tumor nature of the neoplasm will be revealed.
Also, diagnosis of skin tumors is necessary when removing a mole or wart, if these formations begin to change in any way. Today there are quite a lot of methods, for example, histological examination, during which skin tissue is collected for further microscopic examination. The molecular genetic method identifies the genome of the patient's papillomavirus. Dermatoscopy involves a visual method of studying pigmented neoplasms at the initial stage, during which the malignant or benign beginning is determined, whether there is a threat of developing into a malignant tumor. This study is quite accurate.
One of the most accurate is spectrophotometric intracutaneous analysis using the SIAscope technique. Such a device allows you to penetrate and quickly examine various skin formations without a scalpel, which will be transferred to the monitor screen. With its help, you can examine the structure of the tumor, color and concentration of melanin and hemoglobin. All blood vessels will be visible.
Such a study allows us to quickly obtain data on the state of education. The image is enlarged to such a state that a specialist can easily identify any abnormalities.
A special feature of this equipment is that all information about the tumor is stored in memory. The specialist can print a copy and give it to the patient. This storage of results makes it possible to track the dynamics of skin diseases using the method of overlaying results. This system also has an electronic atlas.
Do benign tumors hide danger?
A benign neoplasm can transform into cancer. Diagnosis, study and prevention are dealt with by the medical science of dermatovenereology and the danger can only be determined by a dermatologist or oncologist.
If the formation poses a threat to life, the doctor prescribes radical removal. Further therapeutic treatment or complete removal is determined by benign and malignant signs of the pathology. Scientists have proven that congenital moles and nevi pose the greatest danger, so dermatologists recommend removing neoplasms without delay. Skin pathological changes often cause discomfort and pain, which becomes an additional reason for eliminating the tumor.