Story
The history of creating a drug from a powerful poison has an unusual history. The first mention of the medical use of this toxin dates back to 1980, when physician F. Scott used it in ophthalmology to treat patients with strabismus. He used it to relieve spasm of muscle fibers. Subsequently, drugs based on poison began to be used in neurology. The high effectiveness of Botox led to the fact that already in 1989 the American committee recommended it for use in ophthalmology and neurology. After doctors administered the drug to eliminate neurological and ophthalmological symptoms, a peculiar side effect often occurred, consisting in a decrease in the severity of wrinkles around the eyes and in the forehead. In this regard, since the nineties of the last century, dermatologists began to use Botox to act on the ligaments of the subcutaneous muscle of the neck, eliminate eyebrow asymmetry and carry out complete facial rejuvenation.
The body produces antibodies
In response to Botox, the immune system may produce antibodies, which subsequently reduce its effect.
This phenomenon is provoked by:
- Insufficient interval between injections
. After the procedure, the cosmetologist always tells you when the next time you need to inject the drug. In some cases, clients rush things and try to get into trouble faster. As a result, the body is overloaded with the drug and begins to resist, which leads to the formation of antibodies. Botox “doesn’t work” and patients lose money. - Exceeding dosages.
This happens with inexperienced doctors who cannot choose the right dose for the patient. This provokes addiction and the production of antibodies. In addition, excess medication can negatively affect the result, making the face unsightly - mask-like. - Post-existing botulism.
Botox and its analogues contain botulinum toxin. This poison occurs naturally, forming in improperly preserved mushrooms, cucumbers, canned food and artisanal sausages. If the patient has ever suffered such poisoning, it means that the body has already produced antibodies, and the injections will not work. This happens very rarely. Botulinum toxin poisoning is severe, it is treated in a hospital and patients are aware of the illness.
Application in ophthalmology
Ophthalmologists use Botox in their practice for:
- Muscular-tonic syndromes;
- Blepharospasm, when the patient cannot open his eyelids;
- Hemifacial spasm;
- Myofacial pain syndrome, accompanied by facial pain.
In addition, the toxin helps eliminate tics, nystagmus, pain, strabismus and migraines.
It is contraindicated to prescribe the drug in case of hypersensitivity to it, with myasthenia gravis, while taking antibacterial agents (aminoglycosides, tetracycline), during pregnancy and hemophilia.
Contraindications for cosmetic procedures
There are certain contraindications to the Botox procedure. It is not recommended to drive it when:
- chronic diseases (especially neurological);
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- diseases of the kidneys, liver and lungs;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- oncology.
If a woman is pursuing the goal of getting rid of wrinkles around her eyes, she first needs to find out whether she suffers from eye diseases. For example, high myopia is a contraindication for correction of the periorbital zone.
Mechanism of action
When treating the diseases listed above, both surgical and therapeutic approaches are used. At the same time, the cause of hypertonicity of muscle fibers is not directly affected.
By injecting botulinum toxin, it targets the muscles. Thin needles are used for insertion. The duration of the blockade of nerve impulse transmission to muscle cells reaches six months, after which the poison is destroyed. That is, during this time the muscles are in a relaxed state.
Due to this, Botox helps patients cope with strabismus, blepharospasm, facial wrinkles around the eyes, in the bridge of the nose and forehead.
As a result, unwanted hypertension is eliminated. To maintain the effect, it is enough to repeat the procedure 2-3 times a year. This allows you to eliminate all the symptoms of these diseases. Despite the fact that this drug is based on poison, its use in ophthalmic practice is absolutely safe. This is due to the fact that only a small amount of the substance is injected directly into the problem area. The action of the toxin is local and selective, which completely distinguishes it from other ophthalmic agents.
But there is one thing: the duration of action does not exceed six months, after which it is necessary to repeat the procedure. Unfortunately, the effectiveness of Botox decreases over time.
International units are used to measure the potency of Botox. Depending on the dose, the speed of onset of the effect varies. In small doses, the drug does not begin to act immediately, but after 1-2 weeks. If the doses are average, the effect becomes noticeable after 24-72 hours, with maximum effectiveness observed after two weeks. When using high doses of Botox, in some cases a clinical effect can be observed after 6 hours. For example, for blepharospasm, 20 units of the drug are most often used. If we compare this dosage with the treatment of neurological pathology, when the dose is 5-10 times higher, it becomes clear that there is no talk of a toxic effect of the drug on the body.
Botox and intelligence: do “beauty injections” make you stupid?
Another popular myth associated with botulinum toxin injections is the allegedly extremely negative effect of this drug on intellectual abilities. Critics of aesthetic medicine claim that people who have received “beauty injections” have significantly reduced mental abilities: they say they perceive spoken language and read text worse, and also begin to suffer from a lack of imagination.
Such “experts” claim that there is some connection between facial activity and the thought process. Thus, in their opinion, it is facial expressions that “activate” cognitive abilities and “trigger” the processing of information by the brain. The main argument in this case is the fact that most people who solve some complex problem in their minds actually actively work with their facial muscles: they wrinkle their foreheads, purse their lips, etc. Therefore, as “experts” assure, Botox, by disrupting facial activity, contributes to the fact that a person literally becomes stupid and cannot cope with even the simplest intellectual load.
In fact, of course, all these are conjectures that have nothing to do with reality. If there really was a connection between the activity of facial muscles and intelligence, geniuses and prodigies would have to be classified as monkeys who constantly grimace, and people who are not naturally highly emotional or have excellent control over facial expressions would be classified as fools.
Effect of the procedure
After injecting botulinum toxin into the desired area, it is necessary to apply ice packs or other cooling solution to this area to eliminate swelling. In some cases, redness occurs a few minutes after the injection. Do not touch this area for 12 hours. It is also recommended to rest after the procedure. 2-15 days after the administration of botulinum toxin, a clinical effect can be observed, the speed of its appearance depends on the specific nosology.
To determine the dose of Botox, you need to calculate the volume of muscles that need correction. The duration of relaxation of muscle fibers ranges from 3 to 6 months. For the effect to be sustainable, you need to perform 2-3 injections with a break of 6-9 months. All side effects are temporary and usually disappear within 10-20 days. Their development is associated with the partial spread of the toxin to neighboring muscles. In case of repeated injection, the effect of the drug often increases. In addition, this technique helps restore facial symmetry in case of paresis of certain nerves or muscle aplasia.
I'm embarrassed to ask: 12 important questions about Botox
What is Botox and what botulinum toxins are on the market?
Botox is the most famous brand of drugs based on botulinum toxin, which is a protein neurotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. This is a drug that disrupts the transmission of impulses from the nerve ending to the muscle, thereby relaxing it.
Contrary to popular belief, preparations based on this substance are widely used to solve a wide range of medical problems, and not just in cosmetology. For example, there are drugs based on it to treat muscle spasms, excessive sweating and some types of headaches.
Until recently, in Russia there were six registered drugs based on botulinum toxin type A. A few months ago, another interesting promising drug received registration. I'll tell you a little about each.
Botox, which has become a household name, was one of the first to be introduced into aesthetic medicine by the Irish company Allergan. Registered as a drug for the correction of facial wrinkles in aesthetic medicine. Very popular among specialists and patients.
Dysport - produced by the French company Ipsen Pharma, differs in conversion into units, it has more indications, recommended for the correction of hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). Everyone loved Dysport no less than the previous toxin.
Xeomin is a product of the German company Merz, considered the most purified toxin; storage conditions do not require refrigeration, which is very convenient for clinics and specialists.
Lantox is a toxin from LIBP - Lanzhou Institute of Biological Products, China. It has the most extensive indications for the correction of facial wrinkles.
Relatox - a remedy for, Russia. The first Russian drug based on botulinum toxin. It has an enhanced formula and a long-lasting effect.
Botulax - developed by Hugel Inc. This South Korean drug came to us later than everyone else, but this did not prevent it from taking a strong position in the aesthetic medicine market.
Most recently, the Russian drug Myotox received registration, the first drug in Russia in a reconstituted form, that is, it is already diluted in a bottle.
South Korea was the first to develop such a drug, but due to the difficulty of registration in our country, we could not count on it. Now we have a Russian analogue - we will test it.
When can (and should) inject botulinum toxin?
You can start administering drugs based on botulinum toxin in aesthetic medicine from the age of 18, if there are necessary indications for this. Therefore, do not wait for deep skin creases to form, contact in a timely manner: the sooner, the better.
How painful is this procedure?
The procedure itself can hardly be called painful: the drug is injected with an insulin syringe with a thin needle. But men don’t like to endure discomfort once again - it’s a fact. The pain threshold for men and women is the same, but there is a difference in psycho-emotional status. Men are more sensitive to injections than women. When the drug is administered, they often begin to wrinkle and tighten, which is why sometimes the needle can even fly out. You just need to be patient a little.
How long does the procedure take?
This is a very fast manipulation. After we have consulted the patient and assessed his facial activity, we proceed directly to the procedure, which takes no more than 15-20 minutes. That is, this is the so-called lunch break procedure.
What effect can you expect from Botox injections and how long does it last?
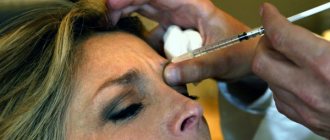
The main aesthetic effect is the smoothing of facial wrinkles in the area between the eyebrows (the so-called “proud wrinkle”), forehead, and around the eyes. Sometimes specialists work with the lower third of the face, correcting the chin and neck area.
The effect lasts from 4 to 6 months, this is written in the instructions for the drugs.
Sometimes in patients who are applying for a similar procedure for the first time, as well as in younger audiences, the effect can last up to 8 months.
What are the features of the Botox procedure specifically for men?
Today, men are increasingly seeking procedures for the correction of facial wrinkles with drugs based on botulinum toxin type A. However, certain features do exist.
- Facial muscles in men are more developed, which is why wrinkles on the skin appear more strongly. In addition, men's eyebrows are on a horizontal line (that is, they do not have such a pronounced bend as women's), and the heads of the eyebrows in the area between the eyebrows droop.
- Men are not recommended to experiment with raising their eyebrows: correction while maintaining a horizontal line looks more natural.
- Requests for correction of wrinkles in the eye area should be treated with caution: this always requires additional discussion with the patient. There are NOT always indications for this. The main risks are worsening hernial protrusions in the lower eyelid or increased swelling around the eyes.
How often should Botox injections be done?
In the classic version, Botox injections are done twice a year - no earlier than 6 months after the last procedure. Typically, patients look at themselves in the mirror, note that their facial expressions have become more active again, and, if necessary, come for a second appointment. In men, the effect of Botox injections wears off on average faster than in women. This is largely due to the fact that their muscles are more powerful and they have greater facial activity.
Is botulinum toxin addictive?
There is no addictive effect. All processes that occur as a result of Botox injections are reversible: over time, innervation and muscle activity return. The main thing is to follow the appointment schedule and not come for the procedure earlier than 4-6 months later. There is such a thing as the production of antibodies. If you do Botox more often than necessary, the body will react accordingly and the patient will become less sensitive to the toxin. Therefore, the recommended frequency is once every six months.
Why does Botox, as they say, not work for some people and can this be detected in advance?
We call this phenomenon insensitivity to the toxin. Indeed, 2−4% of the entire population have this feature, and such patients do occur. The reasons for this are still unknown. It is also not possible to identify this in advance: this can only be revealed after the procedure has been carried out. At the same time, we try several variants of drugs: sometimes it happens that there is no sensitivity to one drug and the desired effect can be achieved by using one of the analogues, which we discussed in detail at the very beginning. If after two attempts with different drugs there is still no effect, you can call it a day. By the way, in men, lack of sensitivity to the toxin is more common, and no one can explain this. Even at an appointment with a specialist, when we assess the patient’s facial activity, we cannot determine that Botox “will not work” for him.
When does the effect of the procedure begin to appear?
This doesn't happen instantly. Only after five days does the toxin begin to act, and we can fully see the result only after 2 weeks. That is, to ensure that the procedure was successful, at least 14 days must pass. By the way, the fact of lack of sensitivity to the toxin can also be detected no earlier than after 2 weeks.
Is there a list of restrictions that must be followed before and after the procedure?
“Before” - here, perhaps, there is only one requirement: it is not advisable to drink alcohol the day before.
“After” - but here there really is a whole series of restrictive measures:
- do not visit the bathhouse or sauna for the first 2 weeks: high temperatures reduce the effect of the toxin and we may not get the desired effect;
- limit sports and yoga to 3-5 days: it is extremely important to avoid standing upside down;
- You cannot take a hot shower immediately after the procedure;
- do not take a horizontal position for the first 4 hours after the procedure, that is, do not lie down;
- do not drink alcohol for 3 to 5 days;
- do not come for the procedure immediately after completing antibiotic therapy: there is a certain group of antimicrobial drugs that weaken the effect of the toxin or negate the effect of its administration. If you have had antibiotic therapy in the recent past, we recommend that you avoid the procedure and return after 2 weeks.
How to understand that the procedure was carried out correctly by a specialist?
If your wrinkles have smoothed out in the areas where correction was carried out, if you have limited movement in the muscles that the specialist relaxed, and at the same time your upper eyelids and eyebrows have not drooped, you have not seen double, or one or both eyes have not “closed” - consider that the procedure was completed successfully.
Undesirable effects periodically occur after the use of a toxin, which are associated with the peculiarities of its mechanism of action. For example, swelling of the eyelids, headaches, asymmetry associated with the gradual effect of the drug. As a rule, they level out within 2-3 weeks.
It happens that the patient does not know about some of his diagnoses, which can cause unwanted side effects during the procedure. For example, myosthenia. If Botox injections are given for this disease, the eye may close - we call this eyelid ptosis. This is reversible. If ptosis does occur and the eyelid is slightly closed, we remove this by prescribing certain medications that reduce the effect of botulinum toxin, as well as with the help of physiotherapeutic procedures.
However, we remember: we get the full picture only after 2 weeks, which means there is no point in sounding the alarm ahead of time and calling the doctor in a panic if 14 days have not passed yet.
It happens that after 2 weeks the effect is insufficient or a slight asymmetry appears - this can be solved by additional injection of the drug.
Technique and features
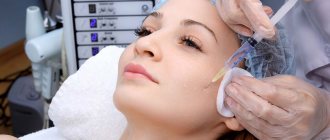
To administer Botox, a thin needle is used, which is placed only at special points in the forehead, eyelids, bridge of the nose, and lateral corners of the eyes.
Before the procedure, you need to conduct a clinical examination (during muscle rest and during facial activity). It is important to pay attention to the effect of raising the eyebrows, asymmetry, as this helps to identify an anomaly.
It is important to carefully collect anamnesis, focusing on the presence of neuropathy, including diabetic or alcoholic.
When administering Botox, it is important to maintain sterile conditions. When treated with this technique, a change in the shape of the eyelids (due to paralysis) and slight drooping of the eyebrows are possible. It is important to note that blepharoplasty after Botox injection has its own characteristics and should take these factors into account. When using the toxin in ophthalmology, many patients note the elimination of tension headaches.
How does Botox work?
Botulinum toxin is a naturally occurring substance produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. The waste product of this bacterium has a powerful neuroparalytic effect, which is what its ability to smooth out wrinkles is based on.
In cosmetology, botulinum toxin type A is used in extremely low concentrations, so its systemic effect on the body is excluded. The mechanism of action is the destruction of chemicals synthesized by nerve fibers and necessary to control striated muscles. As a result of the injection, flaccid paralysis of the muscle into which the toxin was injected occurs and facial wrinkles are smoothed out.
How to prolong the effect
It is important to follow the basic recommendations of cosmetologists. Firstly, this will avoid unpleasant consequences. Secondly, it will help maintain the results longer.
Avoid excessive physical activity. In people with well-developed muscles, the results of botulinum therapy, in principle, disappear faster, and the administered dose should be higher.
Do not “pin up” small doses in the intervals between full procedures. Periodic administration of the toxin in small doses leads to the production of antibodies that destroy it. As a result, Botox stops working completely.
Limit visits to baths, saunas, and solariums. If you take any medications on an ongoing basis, you should inform your doctor in advance. It may turn out that botulinum therapy is not compatible with your medications.
Rules of behavior after injections
In the first 3 days you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Avoid hot baths, baths or saunas.
- Do not visit the solarium or sunbathe under the sun's rays.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Do not take tetracycline antibiotics. muscle relaxants, some analgesics, B vitamins.
- Do not massage the muscles into which the injection was made.
What happens if you stop injecting Botox?
If you adhere to a competent approach to manipulation, observe the correct dosages and time intervals between courses, then stopping botulinum therapy will return the muscle to its natural state at that time.
Of course, if you have had the procedure done for many years, the muscle and skin will not be as “young” as before. Botox does not prevent age-related changes, but only temporarily masks them.
Side effects of Botox
Are common. Typically, adverse reactions occur within the first few days after the injection and are temporary. In rare cases, adverse reactions may last several months or longer. Local muscle weakness is the expected pharmacological effect of botulinum toxin in muscle tissue. As with other injections, adverse reactions may include localized pain, tenderness, and/or hematoma. High fever and flu-like symptoms have also been reported following botulinum toxin injections. In the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis, an increase in non-axillary sweating was observed within 1 month after injection, localization to specific anatomical sites was not evident. This phenomenon stopped within 4 months. Arm weakness was rarely reported (0.7%), was mild, temporary, did not require treatment, and resolved without sequelae. The appearance of this negative effect can be explained by the peculiarities of the treatment procedure, the injection technique, or both reasons at once. In isolated cases of muscle weakness, a neurological examination should be performed. In addition, before further injections, it may be advisable to review the technique of their implementation to ensure their subcutaneous localization. Additional Information. Dysphagia ranged from moderate to severe with the possibility of aspiration, sometimes requiring medical intervention. Adverse effects related to dissemination of botulinum toxin from the injection site have been reported very rarely (pathological muscle weakness, dysphagia, aspiration/aspiration pneumonia, in some cases fatal). Since the drug Botox entered the market, the following side effects have been reported: dysarthria, abdominal pain; blurred vision; hyperthermia; limited facial paralysis; hypoesthesia; discomfort; myalgia; itching; hyperhidrosis; diarrhea; anorexia; hypoacusia; noise in ears; radiculopathy; fainting conditions; myasthenia gravis; exudative erythema multiforme; psoriasis-like dermatitis; vomiting and brachial plexopathy. Cardiovascular side effects, such as arrhythmia and myocardial infarction, some fatal, have also been rarely reported. Some of these patients had risk factors, including cardiovascular disease. Severe immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, serum sickness, urticaria, soft tissue swelling and dyspnea, have been occasionally reported. Some of these reactions have been observed after using Botox alone or with other drugs that have similar adverse reactions. A case of peripheral neuropathy was identified in an elderly man after 4 courses of Botox injections - a total of 1800 IU-Alergan (for the treatment of spasms of the neck and back muscles and severe pain) for 11 weeks. Angle-closure glaucoma has very rarely been reported after botulinum toxin treatment for blepharospasm. Neoplasms or cases of relapse were recorded, as a rule, in patients with a tendency to this. There was no reliable connection between these cases and botulinum toxin injections. The report in children concerned primarily patients with cerebral palsy who were being treated for spasticity. Injection pain and/or fear may result in vasovagal reactions.
Botox drug interactions
Theoretically, the effect of botulinum toxin can be enhanced by aminoglycoside antibiotics or spectinomycin, or other drugs that interfere with neuromuscular transmission (for example, muscle relaxants such as tubocurarine). The effect of using different serological types of botulinum neurotoxin simultaneously or at intervals of several months is not known. Excessive neuromuscular weakness may be exacerbated by the use of another botulinum toxin before analyzing the effect of the previously applied botulinum toxin. No interactions were studied. No clinically significant interactions were reported.
Indications for use of Botox
To eliminate muscle spasms:
- eyelid (blepharospasm);
- face (hemifacial spasm);
- neck and shoulders (cervical dystonia);
- hands and wrists in adults who have had a stroke;
- to regulate equine foot deformities in walking patients with cerebral palsy aged 2 years and older;
For treatment and elimination:
- primary hyperhidrosis of the armpits, which interferes with work and is not subject to local treatment;
- vertical wrinkles between the eyebrows (moderate to severe) in adults under 65 years of age.